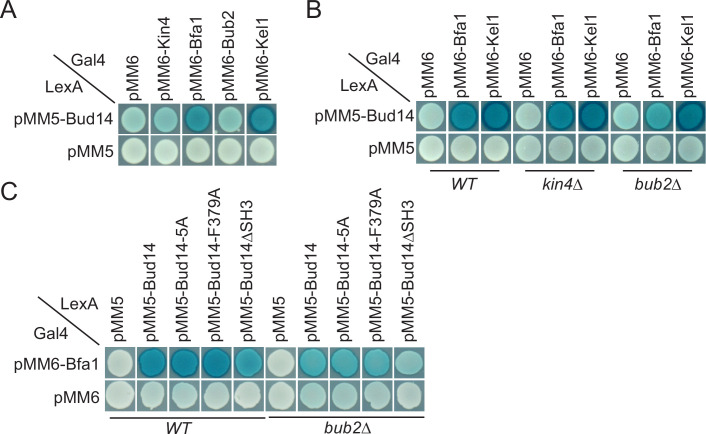
Figure 5. Yeast two hybrid analysis of Bud14 and Bud14 mutants with spindle position checkpoint (SPOC) proteins.
(A) Bud14 interacts with Bfa1 but not with Bub2 or Kin4. (B) Bud14-Bfa1 interaction is dependent on Bub2. (C) Bfa1-Bud14 interaction is reduced in Bud14∆SH3 mutant. SGY37 was co-transformed with indicated plasmids. Empty plasmids served as a control for any self-activation. Kel1 served as a positive control. Cells were grown for 2 days on selective agar plates before overlay. Blue color formation was monitored as an indication of protein-protein interaction.
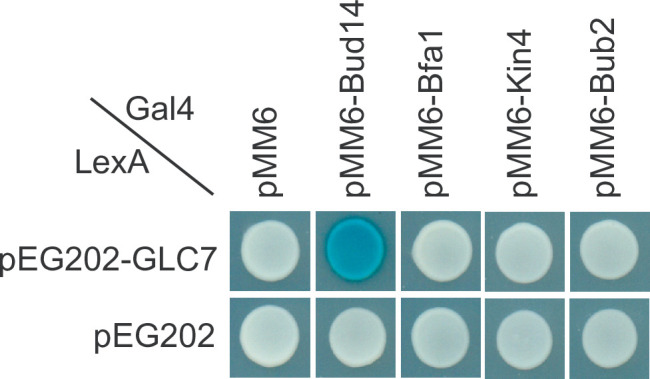
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Analysis of Glc7 interaction with spindle position checkpoint (SPOC) components.