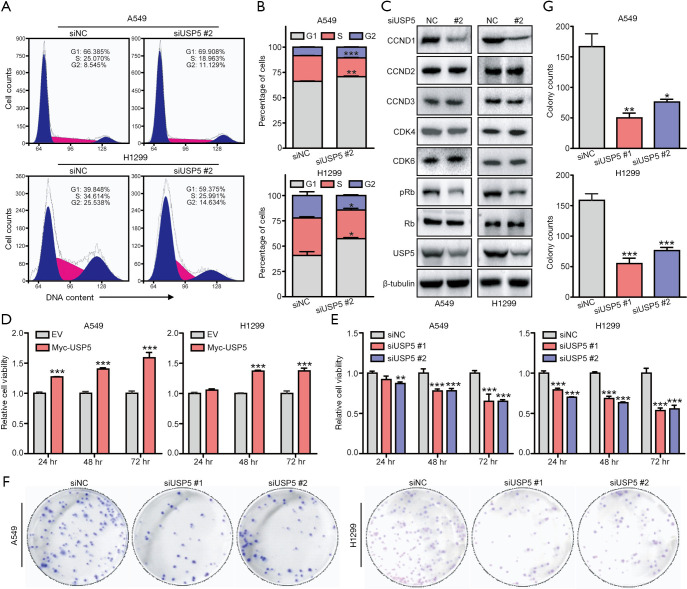
Figure 3.
USP5 promotes cell cycle progression and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. (A,B) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with siUSP5 or siNC (150 nM) for 48 hours. Cell cycle phases were then analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative images of flow cytometric cell cycle analysis (A) and the percentage of cells in each cell cycle phase distribution (B) are shown. G1 or S in A549: G1, **, P<0.01 or S, ***, P<0.001; G1 or S in H1299: *, P<0.05, Student’s t-test. (C) In A549 and H1299 cells, the levels of proteins involved in the CCND1-CDK4-Rb signaling pathway after knockdown of USP5 were assessed by immunoblotting (IB) assay using the indicated antibodies (Abs) [primary Ab: anti-CCND1, 1:1,000, anti-CCND2, 1:1,000, anti-CCND3, 1:1,000, anti-CDK4, 1:1,000, anti-CDK6, 1:1,000, anti-pRb (Ser780), 1:1,000, or anti-Rb, 1:1,000; secondary Ab: horseradish peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG, 1:2,000]. (D,E) Myc-USP5- and siUSP5-transfected A549 and H1299 cells along with the respective control cells were cultured for different time periods (24–72 hours), and cell viability was then measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. **, P<0.01 or ***, P<0.001 compared with their respective control at the same time point, Student’s t-test. (F,G) Colony formation assay was performed using siUSP5-tranfected A549 and H1299 cells and their respective control cells. Representative images of colony formation assay (F) and the number of colonies (G) are shown. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, or ***, P<0.001 compared with the respective control, Student’s t-test.