Figure 1.
Expression and subcellular localization ofNSP3 proteins ofSARS-CoVand SARS-CoV-2
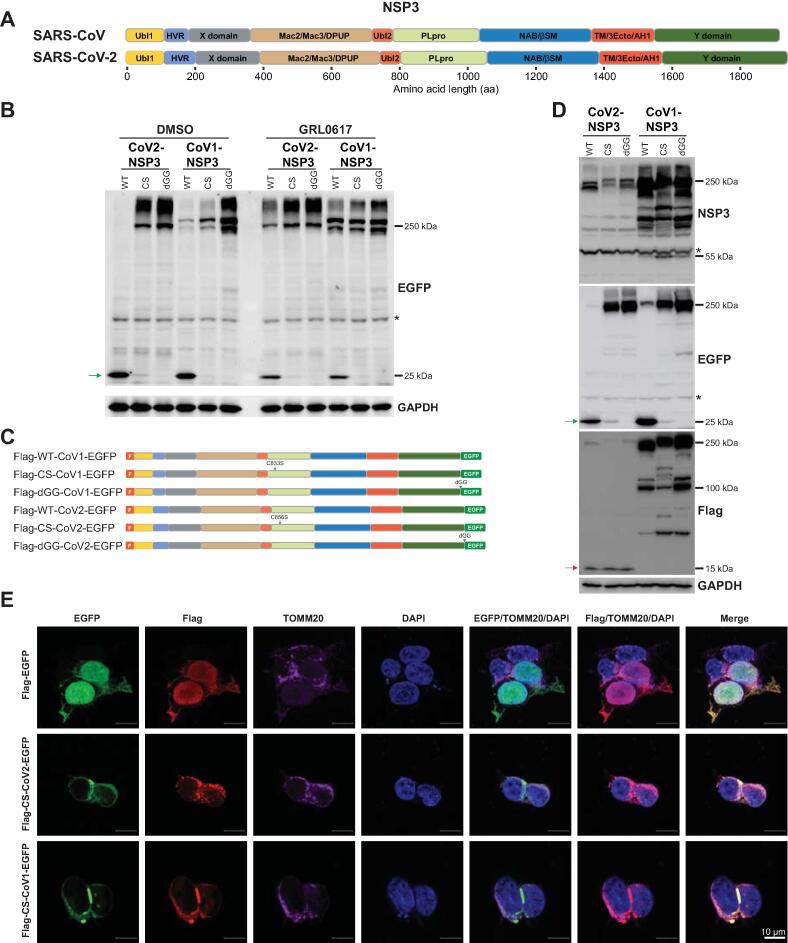
A. Schematic illustration of NSP3 proteins of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Domains of NSP3 proteins of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 are illustrated according to Lei et al. [15] and Alhammad et al. [16]. B. GRL0617 inhibits the release of C-terminal EGFP from NSP3-EGFP proteins. Cells transfected with indicated plasmids (Figure S1A) were treated with DMSO or GRL0617 for 24 h. Cells were lysed and anti-EGFP antibody was used for immunoblotting. Green arrow indicates the released EGFP protein, and asterisk indicates non-specific signal. GAPDH was used to serve as a loading control. C. Schematic illustration of plasmids used in (D). D. CoV2-NSP3 is processed at the N-terminus. Green arrow indicates the released EGFP, and red arrow around 15 kDa indicates the processed N-terminus of CoV2-NSP3. Asterisks indicate non-specific signals. E. N-terminus of CoV2-NSP3 prefers to co-localize with the mitochondrial marker TOMM20. HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-CoV1/2-NSP3-EGFP plasmids were fixed 48 h post-transfection. Anti-Flag and anti-TOMM20 antibodies were used to visualize the co-localization. Scale bar, 10 μm. NSP3, non-structural protein 3; SARS-CoV, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; Ubl1, ubiquitin like domain 1; HVR, hyper variable region; X/Mac1, macrodomain I; Mac2/Mac3/DPUP, macrodomain II, macrodomain III, and domain preceding Ubl2 and PLpro; Ubl2, ubiquitin like domain 2; PLpro, Papain-like protease; NAB/βSM, nucleic acid-binding and beta-coronavirus-specific marker domain; TM/3Ecto/AH1, transmembrane region, 3 ectodomain, and amphipathic helix1; Y, a domain with unknown functions; EGFP, Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CoV1-NSP3, NSP3 of SARS-CoV; CoV2-NSP3, NSP3 of SARS-CoV-2; WT, wild-type NSP3; CS, catalytic inactivated NSP3; dGG, GlyGly deficient NSP3; F, Flag; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.