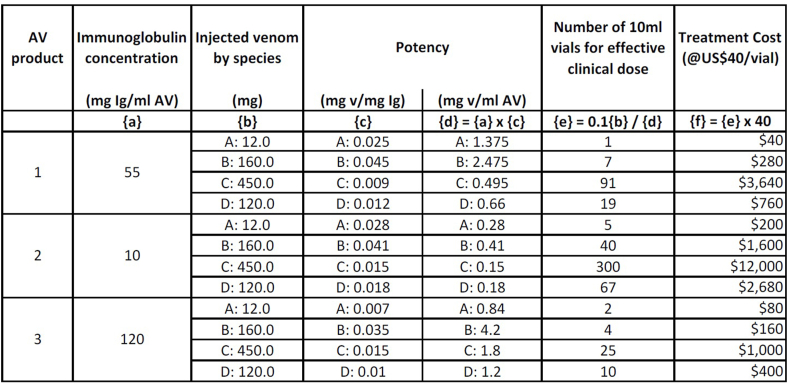
Fig. 3.
Hypothetical immunoglobulin content and potency of three antivenoms (1, 2, 3) against four venoms (A, B, C, D), with estimated impact on dose and cost of effective treatment. While snakes generally inject less venom in defensive bites than they do when venom is extracted in the laboratory, using average venom yield as the basis for initial dose estimation ensures that every patient receives a clinically effective dose as soon as possible. Products 1 and 2 would be ineffective against venom C (product 2 also ineffective against venom D). Product 3 with the highest immunoglobulin content could be effective at volumes of 20–250 ml against all four species, but at a cost ranging from US$80–1000 per treatment, depending on the species. Acronyms: mg Ig/ml AV = milligrams of immunoglobulin per milliliter of antivenom; mg v/mg Ig = milligrams of venom neutralized by 1 mg of immunoglobulin; mg v/ml AV = milligrams of venom neutralized by 1 mL of antivenom.