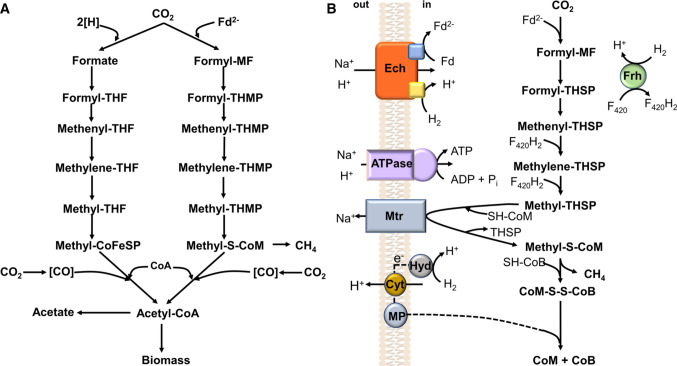
Fig. 1.
The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway of acetyl-CoA formation from CO2 in acetogenic bacteria (A, left) and methanogenic archaea (A, right). In the anabolic route, acetyl-CoA is further converted to pyruvate and from there into the different biosynthetic routes. In the catabolic routes, acetate and methane are the end products (modified after Ljungdahl 1986; Welte and Deppenmeier 2014). B The carbon and electron flow in methanogenesis coupled to ATP synthesis by a chemiosmotic mechanism in cytochrome-containing Methanosarcina species (modified after Welte and Deppenmeier 2014). The ion specificity of the ion-translocating enzymes is shown, but the stoichiometry is not indicated since it is unknown. [H], reducing equivalent, one electron; cyt, cytochrome; MP, methanophenazine; F420, coenzyme F420; F420H2, reduced coenzyme F420; Frh, coenzyme F420 reducing hydrogenase; Mtr, methyl-THSP:CoM methyltransferase