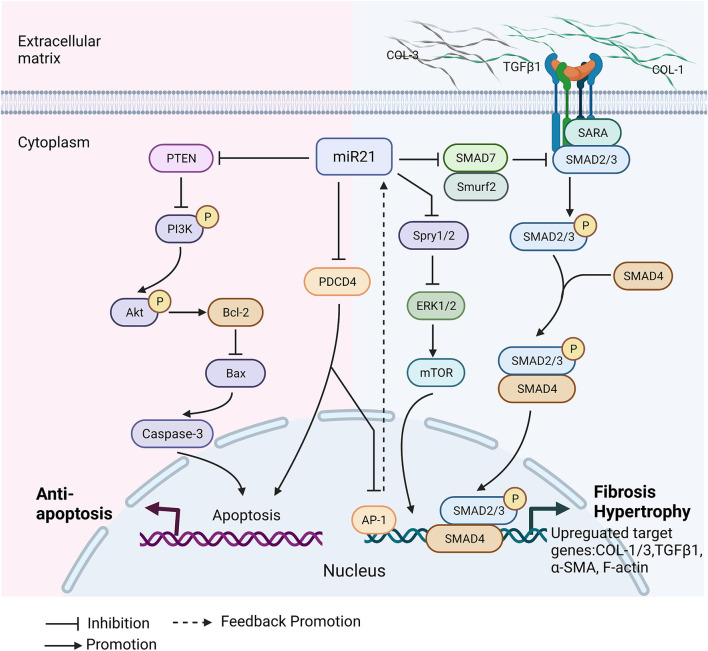
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of miR-21 involvement in cardiomyopathies. Cardiomyopathy alters miR-21 expression level in heart and circulation. miR-21 has protective effects on heart in cardiomyopathy. It regulates cardiac cell death by targeting PTEN and PDCD4. There is a positive promotion loop between miR-21 and AP-1. Overexpression of miR-21 inhibits PDCD4, and further increases AP-1, which is a transcription factor directly promotes miR-21 expression. PTEN downregulation activates PI3K/Akt pathway to promote cardiomyocytes survival and proliferation, that can protect against heart dysfunction. In the meantime, miR-21 has also negative effects on cardiac diseases' development. miR-21 regulates smad7/smad2/3 and Spry/ERK pathways to promote cardiac fibrosis by increasing collagens deposition, TGFβ1, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and filamentous actin (F-actin) polymerization. Spry/ERK/mTOR pathway contributes to myocardial hypertrophy through increasing myofibroblast survival. Collagen type I/III (COL1/3), PTEN, Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K), Protein kinase B(Akt), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), bcl-2-like protein 4 (Bax), Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4), Activator protein 1(AP-1), Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), Sprouty 1/2(Spry 1/2), Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), SMAD Specific E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 2 (Smurf 2), Smad anchor for receptor activation (SARA), SMAD Family Member 2/3/4/7 (Smad2/3/4/7), Filamentous actin (F-actin), Alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). This figure is created with BioRender.com.