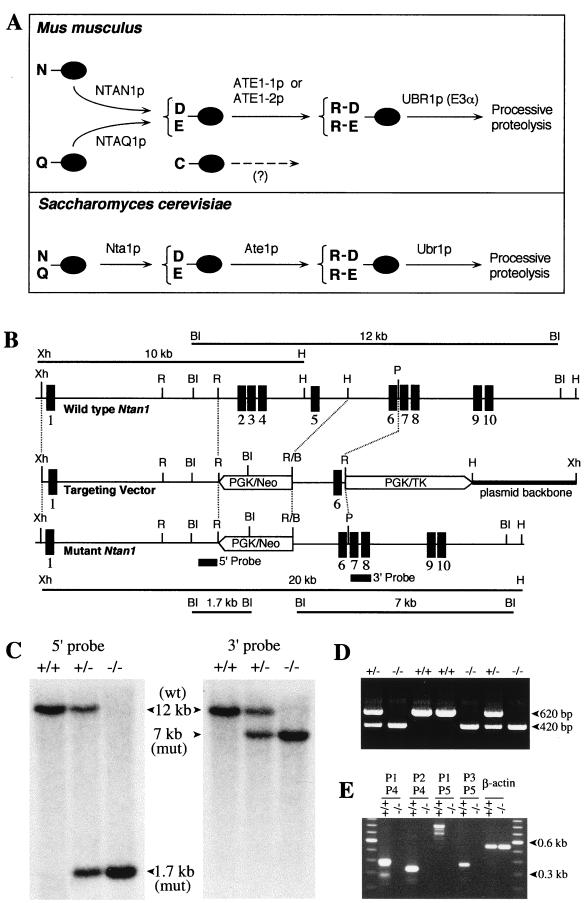
FIG. 1.
Deletion-disruption of the mouse Ntan1 gene. (A) Comparison of enzymatic reactions that underlie the activity of tertiary and secondary destabilizing residues in the yeast S. cerevisiae and the mouse. N-terminal residues are indicated by single-letter abbreviations for amino acids. The ovals denote the rest of a protein substrate. The Ntan1-encoded mammalian NtN-amidase converts N-terminal Asn to Asp. N-terminal Gln is deamidated by NtQ-amidase, which remains to be isolated (see text). In contrast, the yeast Nt-amidase Nta1p can deamidate either N-terminal Asn or Gln (6). The secondary destabilizing residues Asp and Glu are arginylated by the mammalian ATE1-1p or ATE1-2p R-transferase (34). A Cys-specific mammalian R-transferase (23) remains to be identified. N-terminal Arg, one of the primary destabilizing residues, is recognized by N-recognin, the E3 component of the N-end rule pathway (63). (B) Targeting strategy. Top, partial restriction map of the mouse Ntan1 gene; middle, structure of the targeting vector; bottom, structure of the deletion-disruption Ntan1− allele. Exons are denoted by solid vertical bars. The directions of transcription of the neo and tk genes are indicated. Homologous recombination resulted in the replacement of the Ntan1 exons 2 to 5 with the neo cassette. Probes for Southern hybridization are indicated by solid rectangles. Restriction sites: Xh, XhoI; R, EcoRI; BI, BamHI; H, HindIII; P, PstI. (C) Southern analysis of BamHI-digested tail DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (Ntan1+/−), and Ntan1−/− mice. The 5′ probe yielded the 12- and 1.7-kb Ntan1 fragments for the wild-type (wt) and mutant (mut) Ntan1 alleles, respectively; the 3′ probe detected 12- and 7-kb fragments. The organization of the deletion-disruption allele was independently verified by Southern analysis of the XhoI-HindIII-digested tail DNA (data not shown). (D) PCR analysis of tail DNA. The primers were 5′-GCCACTTGTGTAGCGCCAAGTGCCAGC (for neo, forward), 5′-CTTCCCACCAAGCCTGACTGTTGATC (for Ntan1, forward) and 5′-CTTCAATTTCTGTGCTCAGCTAAGCTC (for Ntan1, reverse). (E) RT-PCR analysis of the total RNA isolated from +/+ and Ntan1−/− EF cells, using primers P1 (for exon 1), P2 (exon 2), P3 (exon 6), P4 (exon 5), and P5 (exon 10). β-Actin mRNA was used as a control, at the 20-fold-lower primer concentration in comparison to other lanes.