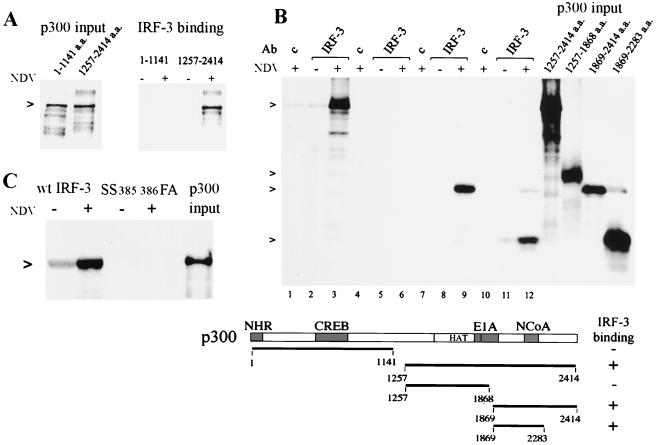
FIG. 2.
Specific binding of IRF-3 to the carboxyl region of p300 in vitro. (A) Amino-terminal (a.a. 1 to 1141) or carboxyl-terminal (a.a. 1257 to 2414) p300 fragments were synthesized in vitro in the presence of [35S]methionine. Lanes on left display relative input of p300. IRF-3 was isolated by immunoprecipitation from HEC-1B cells uninfected or infected with NDV, and the immunocomplexes were incubated with p300. (B) Various carboxyl-terminal fragments of p300 were generated (relative input is shown on the right) and were tested for binding to IRF-3 as in panel A: lanes 1 to 3, a.a. 1257 to 2414; lanes 4 to 6, a.a. 1257 to 1868; lanes 7 to 9, a.a. 1869 to 2414; lanes 10 to 12, a.a. 1869 to 2283. A diagrammatic representation of the results is shown in the lower panel. Domains of p300 known to bind to nuclear hormone receptors (NHR), cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB), adenoviral E1A oncoprotein (E1A), and NcoA are shown. The histone acetyl transferase domain is also noted (HAT). (C) In vitro binding to p300 (a.a. 1257 to 2414) was tested for the IRF-3 mutation (SS385/386FA). The right lane displays relative input of p300.