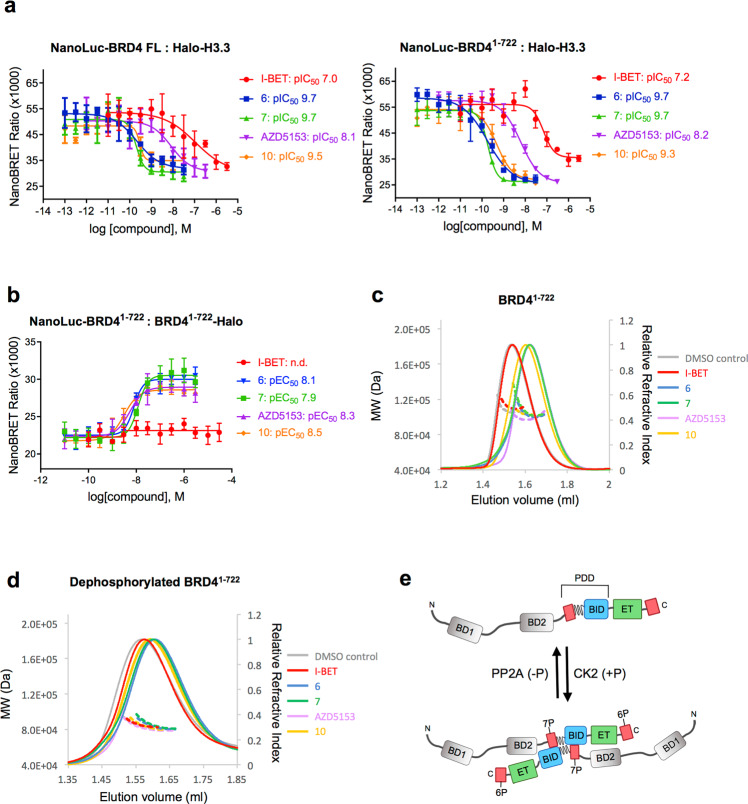
Fig. 6. biBET inhibitors induce BRD4 compaction in vitro and in cells.
a Effects of increasing concentration of bivalent compounds versus monovalent I-BET on the interaction between H3 and BRD4 full length or H3 and BRD41–722 measured by NanoBRET. The mean with SD is reported (n = 4 independent experiments). b Effects of increasing concentrations of bivalent compounds versus monovalent I-BET on BRD41–722 dimerization. The mean with SD is reported (n=4 independent experiments). c Effects of the addition of biBET inhibitors on the SEC-MALS elution profiles of BRD41–722 produced in insect cells (phosphorylated) or d produced in insect cells and treated with λ-phosphatase (dephosphorylated). e Model of BRD4 dimerization driven by CK2 phosphorylation. The isoform C of BRD4, used in the study, is depicted. The NPS and CPS regions are represented as red boxes, the coiled-coil region (aa 506-530) is drawn as a wavy line and the phosphorylation-dependent dimerization domain (PDD) comprising NPS, the coiled-coil region and BID, is highlighted. The proposed conformation of the dimer is head to tail. Compounds are labeled as follows: I-BET red-circle and line; compound six blue square and line, compound seven green triangle and line, AZD5153 purple inverted triangle and line, compound 10 orange rhombus and line, DMSO control grey line.