FIGURE 5.
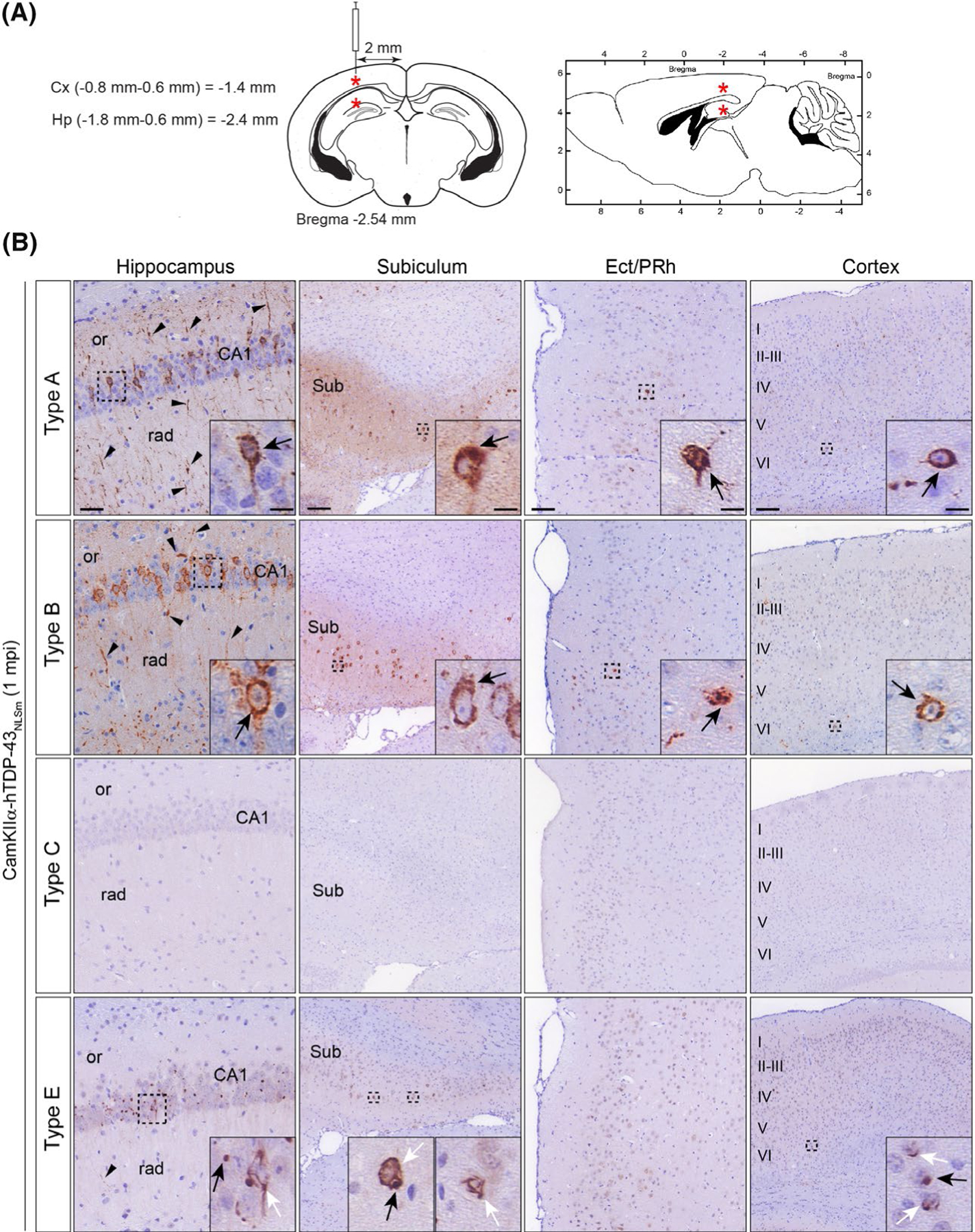
Brain-derived TDP-43 strains from different FTLD-TDP subtypes have distinct seeding properties in vivo. (A) Schematic illustrations of coronal and sagittal brain sections (left and right respectively) with coordinates used for the stereotaxic injections into the brains of CamKIIa-hTDP-43NLSm mice. Red asterisks indicate the injection site in the hippocampus and overlying cortex. (B) Representative photomicrographs of p409–410 immunostaining of phospho-TDP-43 in coronal brain sections from CamKIIa-hTDP43NLSm mice stereotaxically injected with human brain-derived TDP-43 protein extracts from different FTLD-TDP subtypes; type A, type B, type C and type E at 1 mpi. Images show p409–410-positive staining in the ipsilateral hippocampus (cornu amonis (CA1 layer), stratum radiatum (rad), and oriens (or)), in the subiculum (Sub), in the ectorhinal/perirhinal cortex (Ect/PRh) and neocortex (cortex, layers I–VI). Black arrowheads point to p409–410-positive neuronal processes in the neuropil. Insets show higher magnifications of the black-dashed boxes. In type A and B injected mice, black arrows point to neurons with intensely stained cytoplasmic p409–410-positive aggregates. In type E injected mice, black arrows point to p409–410-positive dot-like inclusions and white arrows point to p409–410-positive skein-like aggregates
