FIGURE 6.
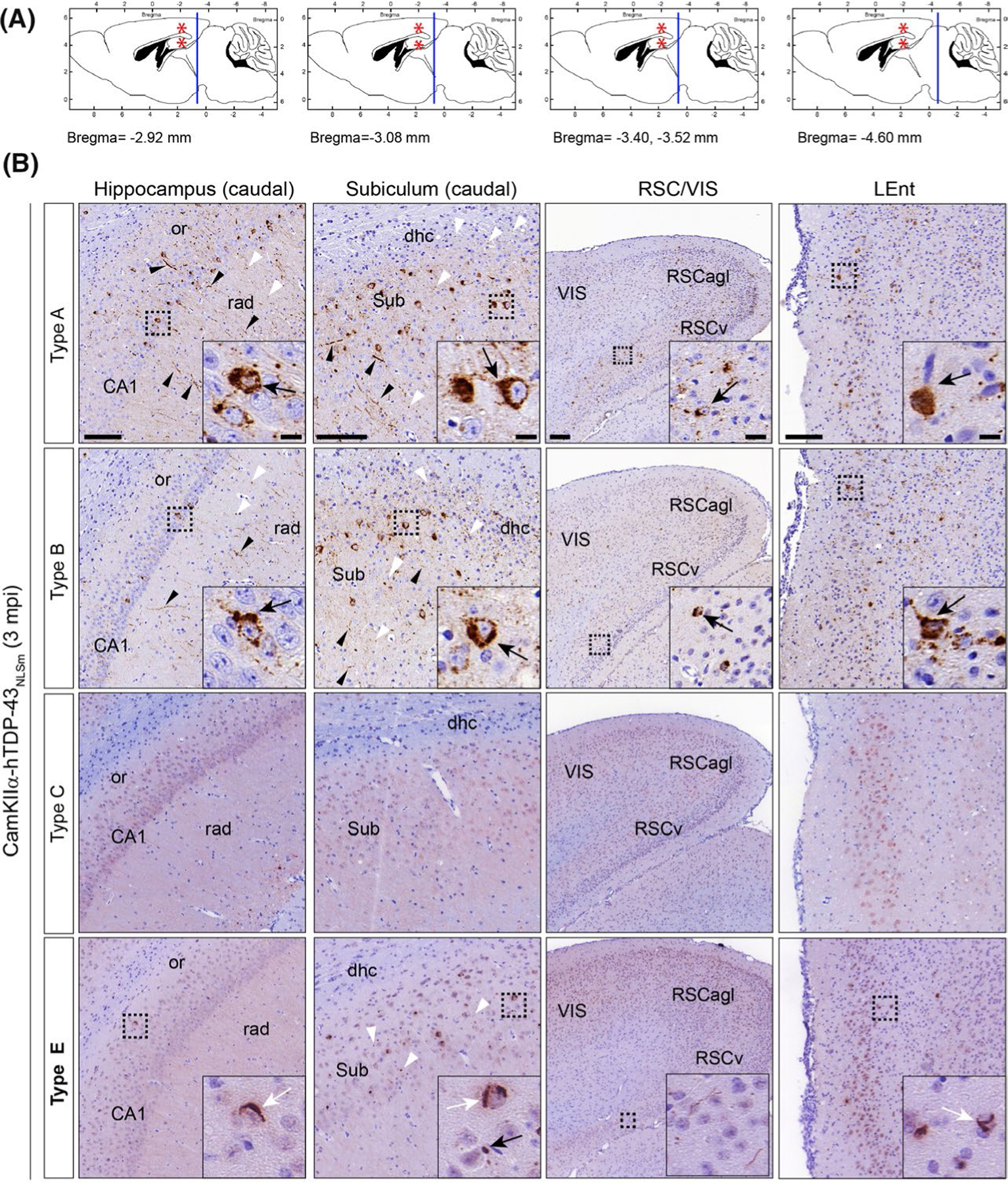
TDP-43 pathology induced in the brain of CamKIIa-hTDP-43NLSm mice injected with brain-derived TDP-43 from different FTLD-TDP subtypes exhibited distinctive spreading patterns over-time. (A) Panels illustrate sagittal brain views of the mouse brain. The red asterisks indicate the injection site in the hippocampus and overlying cortex. Blue lines indicate the localization of the coronal brain sections corresponding to images in B; hippocampus (caudal) (Bregma −2.92 mm), subiculum (caudal) (Bregma −3.08 mm), restrosplenial cortex and primary visual cortex (RSC/VIS) (Bregma −3.40 and −3.52 mm), and lateral entorhinal cortex (LEnt) (Bregma −4.60 mm). (B) Representative photomicrographs of mAb p409–410 immunostaining in coronal brain sections from CamKIIa-hTDP43NLSm mice stereotaxically injected with human brain-derived TDP-43 from different FTLD-TDP subtypes; type A, type B, type C, and type E at 3 mpi. Images show p409–410 positive staining in the ipsilateral side of the brain, in caudal areas distal from the injection site such as; hippocampus (cornu amonis (CA1 layer), stratum radiatum (rad), and oriens (or)), subiculum (sub) and including the dorsal hippocampal commissure (dhc), ventral and lateral agranular RSC (RSCv and RSCagl), VIS and LEnt. Black arrowheads point to p409–410 positive short and long neurites and white arrowheads to dotted staining in the neuropil. Insets show higher magnifications of the black-dashed boxes; in type A and B injected mice, black arrows point to neurons with widespread cytoplasmic p409–410 positive aggregates whereas in type E injected mice, black arrows point to dot-like inclusions and white arrows skein-like aggregates. Scale bar = 100 μm, and 10 μm (insets)
