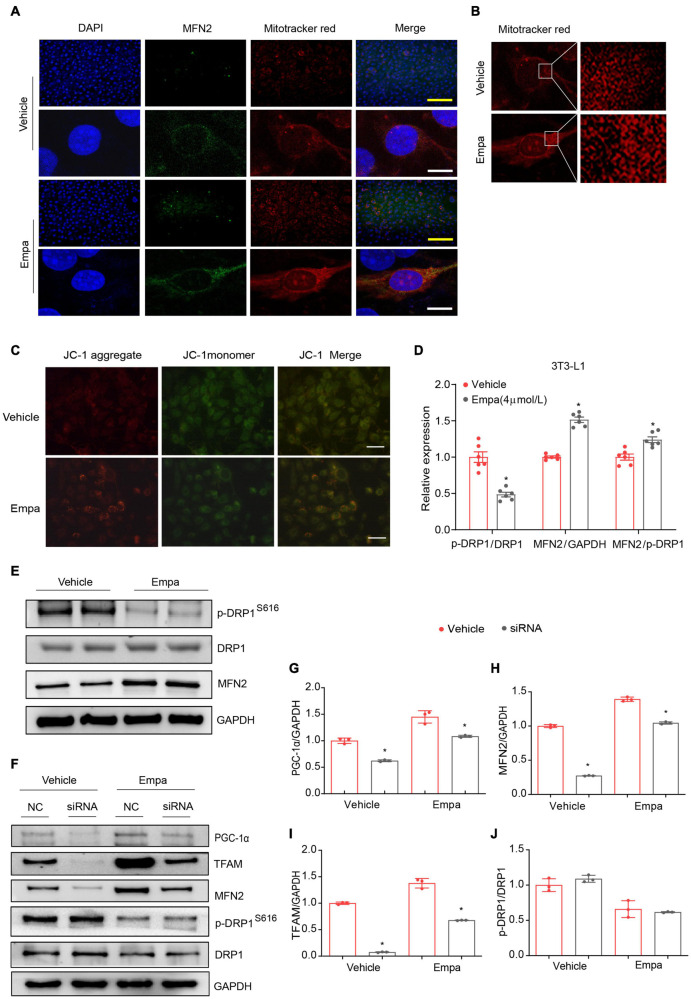
FIGURE 7.
Empagliflozin induces mitochondrial fusion via PGC-1α and increases mitochondrial membrane potential in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with (Empa) or without (Vehicle) empagliflozin (4 μmol/L). (A) Immunofluorescence staining of mitochondria with MitoTracker Red (red) and of MFN2 (green) with nuclei stained blue with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI); and (B) mitochondria stained with MitoTracker Red under confocal microscopy. Immunofluorescence scale bar represents 10 μm, Immunoconfocal scale bar represents 200 μm. (C) Analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential with JC-1. Representative images of JC-1 aggregates (red), monomers (green), and both aggregates and monomers. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (D,E) Western blot and quantitation of p-DRP1 (S616), DRP1, and MFN2, with GAPDH used as a loading control. (F–J) Mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes were transfected with negative control small interfering RNA (siRNA; NC) or Pgc-1α siRNA (siRNA) for 24 h and then treated with (Empa) or without (Vehicle) empagliflozin (4 μmol/L) for 72 h. Western blot and quantitation of PGC-1α, TFAM, MFN2, and DRP1, with GAPDH used as a loading control. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. NC.