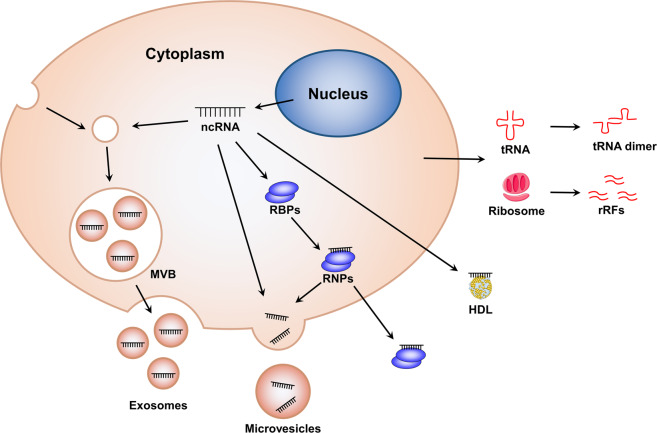
Fig. 3.
Different mechanisms underlying the stability of extracellular ncRNAs. NcRNAs can be protected from harsh extracellular environment through extracellular vesicles encapsulation (such as exosomes and microvesicles), ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex formation, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) transportation. Moreover, some extracellular RNA fragments that generate from non-vesicular ncRNAs in extracellular space can form self-protecting dimers. The source of these non-vesicular RNAs remains uncertain. This figure was created with the aid of Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/). MVB multivesicular bodies, RBPs RNA-binding protein, rRFs rRNA-derived fragments