Figure 4. Repressor sequences that can repress bond expression in the EB hwe and hb are present in all species tested, including species that do not express bond in the EB.
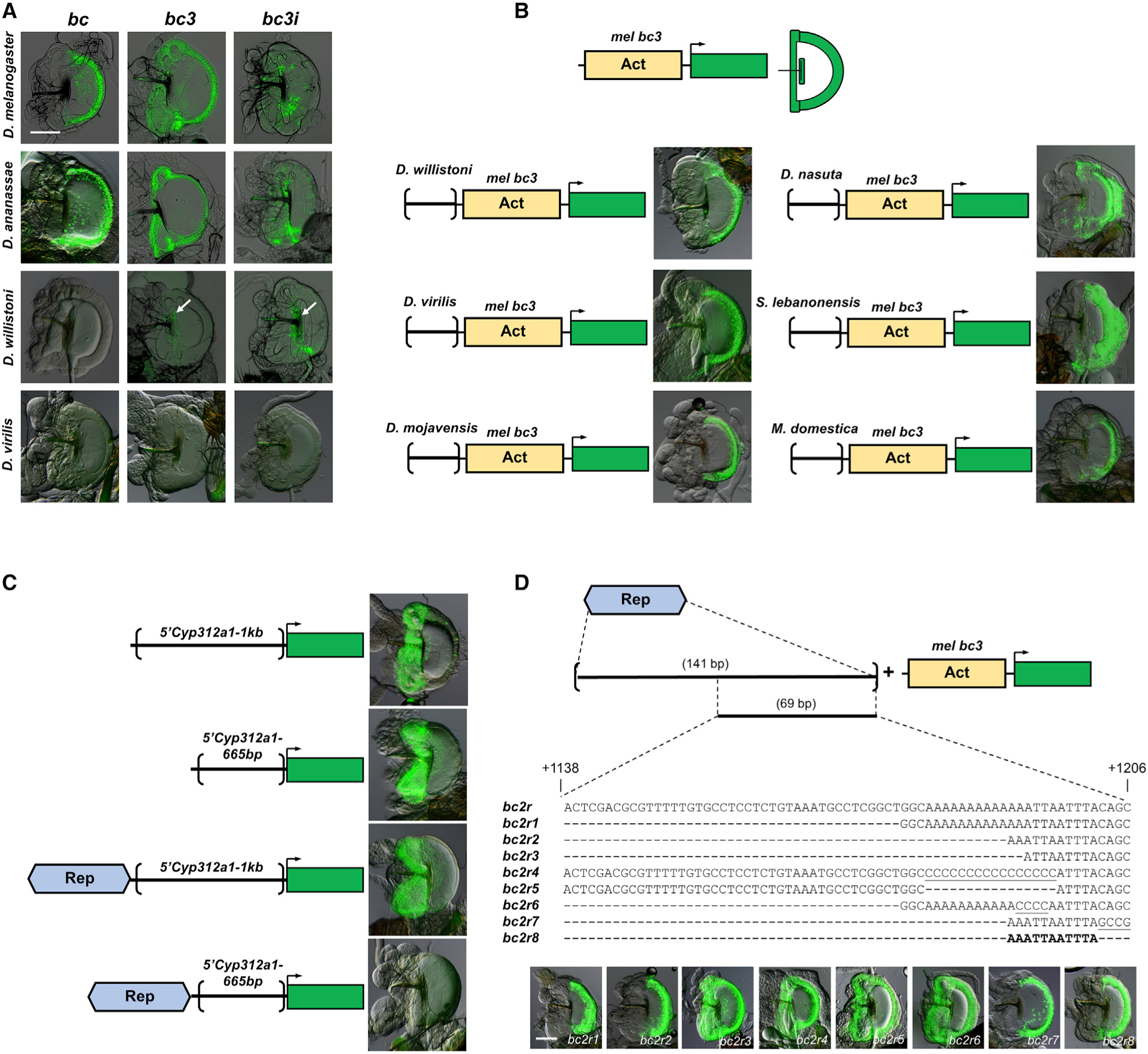
(A) The larger bc fragment recapitulates the native expression of bond in the EB in D. melanogaster and D. ananassae and showed no EB GFP expression with D. willistoni and D. virilis homologous constructs, similar to their native expression. However, the smaller D. willistoni bc3 and bc3i constructs could drive GFP expression in the handle base (white arrows), similar to the bc3i construct of D. melanogaster, suggesting the presence of repressor sequences in the larger bc construct of this species. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) Homologous sequences to the D. melanogaster Rep region from six other species, D. willistoni, D. virilis, D. mojavensis, D. nasuta, S. lebanonensis, and M. domestica, can repress GFP expression in the hwe and hb driven by the mel bc3 fragment, suggesting that these regions contain repressor sequences similar to the D. melanogaster Rep region.
(C) The D. melanogaster Rep region can repress EB GFP expression in the hwe and hb driven by another activator sequences from another gene, Cyp312a1, in a distance-dependent manner.
(D) A series of deletion and mutation constructs are made for the 141-bp Rep region of D. melanogaster. The mutated nucleotides are underscored. A 11-bp sequence (5′-AAATTAATTTA-3′) is able to repress GFP expression in the hwe and hb driven by the mel bc3 fragment. Scale bar, 100 μm.
