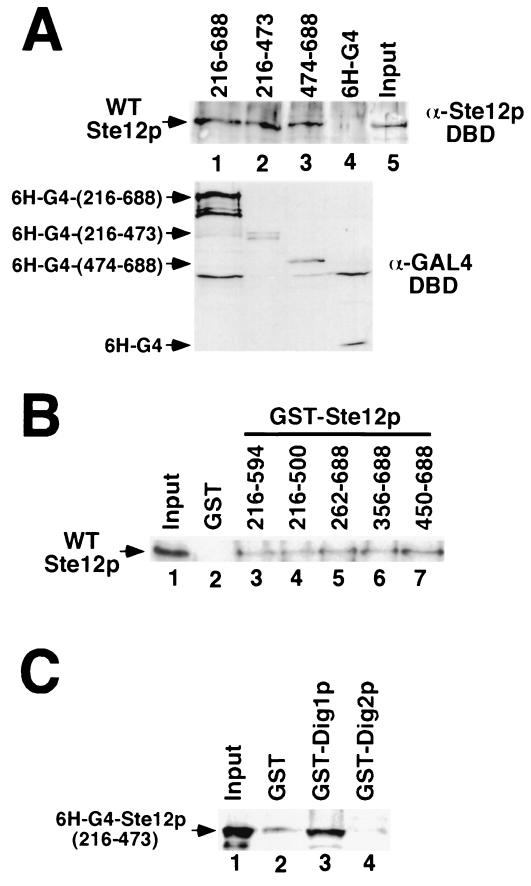
FIG. 7.
Ste12p C-terminal regions cause multimerization in vitro. (A) WT Ste12p SF9 extracts (input, lane 5) were incubated with extracts from E. coli expressing His6-tagged Gal4p DBD (6H-G4, lane 4) or 6H-G4 fused to Ste12p residues 216 to 688 (lane 1), 216 to 473 (lane 2), or 474 to 688 (lane 3). Gal4p fusions were recovered by immunoprecipitation with GAL4 DBD monoclonal antibody, and the interacting Ste12 protein was detected by Western blotting with Ste12p(1–215) antibodies (top). Input 6H-G4 fusion protein was detected by Western blotting with Gal4p DBD antibodies (bottom). (B) WT Ste12p-containing extracts (input, lane 1) were incubated with recombinant GST (lane 2) or GST fused to residues 216 to 594 (lane 3), 216 to 500 (lane 4), 262 to 688 (lane 5), 356 to 688 (lane 6), or 450 to 688 (lane 7) of Ste12p. Bound WT Ste12p recovered with glutathione-agarose was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with Ste12p DBD antibodies. (C) Extracts from E. coli expressing His6-Gal4p fused to Ste12p(216–473) (input, lane 1) were incubated with recombinant GST (lane 2), GST-Dig1p (lane 3), or GST-Dig2p (lane 4). Bound 6H-G4–Ste12p recovered with glutathione-agarose was detected by immunoblotting with Gal4p DBD antibodies.