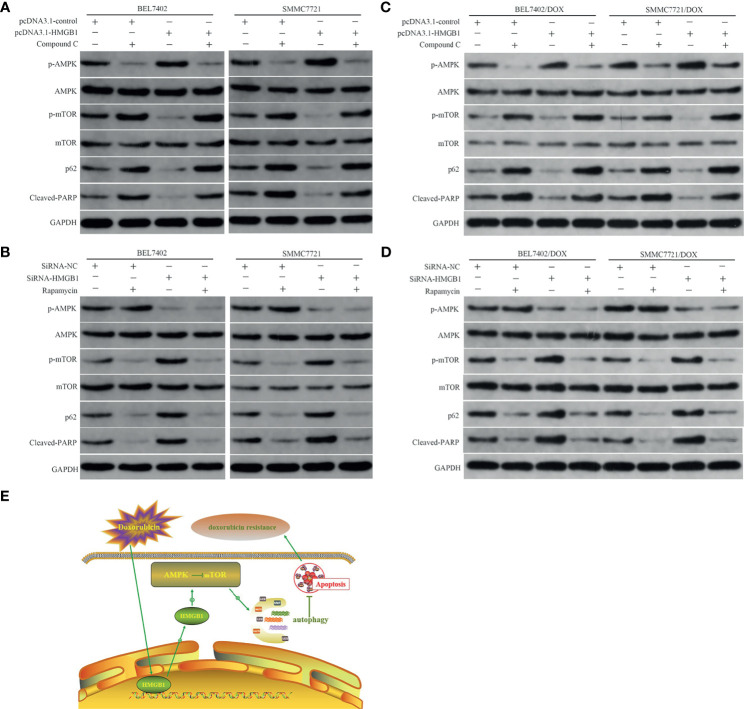
Figure 5.
HMGB1-mediated autophagy that downregulates apoptosis in HCC cells involves the AMPK/mTOR pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, p62, and apoptosis-related protein cleaved PARP in BEL7402 and SMMC7721 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-control or pcDNA3.1-HMGB1 and then pretreated with or without AMPK inhibitor Compound C (10μM). (B) Western blot analysis of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, p62, and cleaved PARP in BEL7402 and SMMC7721 cells transfected with siRNA-HMGB1 or siRNA-NC and then treated with or without mTOR inhibitor rapamycin(10 nM). (C) Western blot analysis of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, p62, and apoptosis-related protein cleaved PARP in DOX-resistant BEL7402 and SMMC7721 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-control or pcDNA3.1-HMGB1 and then pretreated with or without AMPK inhibitor Compound C. (D) Western blot analysis of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, p62, and cleaved PARP in BEL7402/DOX and SMMC7721/DOX cells transfected with siRNA-HMGB1 or siRNA-NC and then treated with or without mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. (E) Model depicting the mechanism by which HMGB1 modulates doxorubicin resistance by inducing autophagy. Doxorubicin induces the cytosolic translocation of HMGB1, which promotes autophagy that decreases apoptosis and increases doxorubicin resistance by activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway.