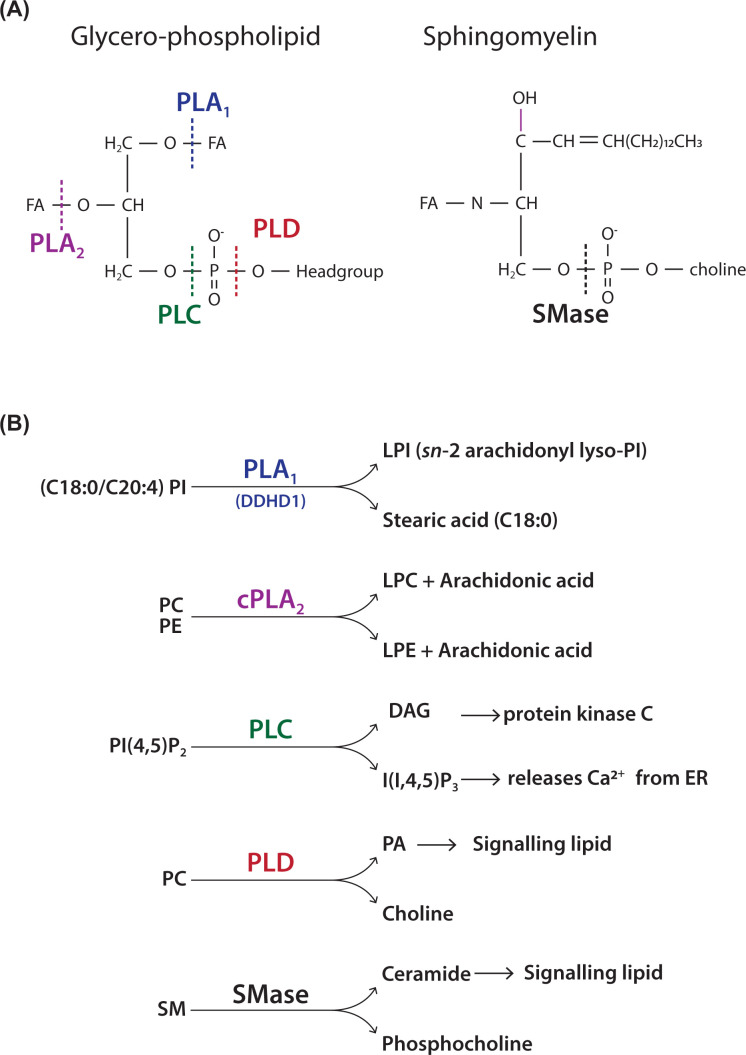
Figure 14. Action of phospholipases on phospholipids.
(A) Site of action of various phospholipases (A1, A2, C and D) on a typical glycerol-phospholipid. The FAs at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions are removed by phospholipases A1 and A2 respectively. Phospholipase C and D attack the phosphodiester bond at different positions. Site of action of sphingomyelinase (SMase) on SM. SMase attacks the phosphodiester bond. (B) Examples of well-known phospholipases that cleave specific substrates. Phospholipase A1 removes stearic acid from PI to make sn-2 arachidonyl lyso-PI, a potent signalling molecule. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) removes arachidonic acid from either PC or PE used for the synthesis of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes. Phospholipase C hydrolyses PI(4,5)P2 that generates two second messengers, I(1,4,5)P3 and DAG. Phospholipase D hydrolyses PC to make PA and choline. SM can be attacked by SMase to make ceramide and phosphocholine.