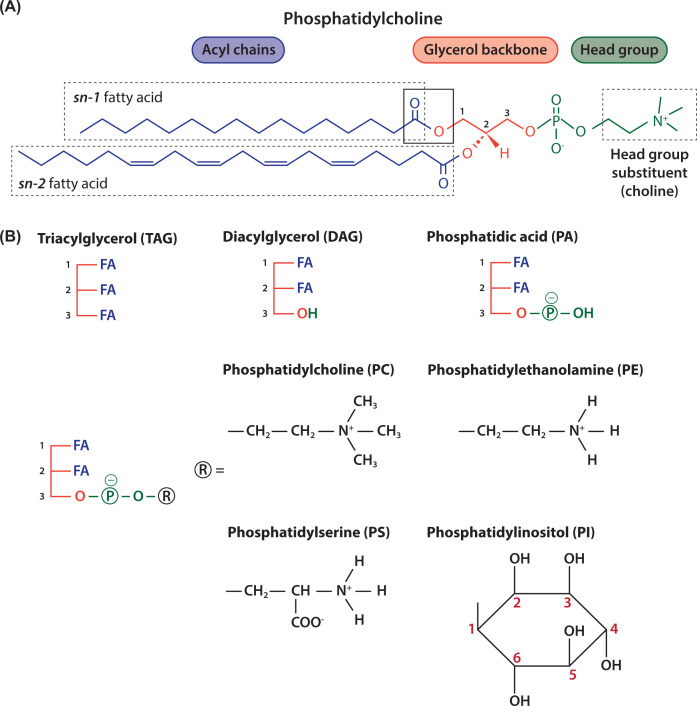
Figure 2. Schematic representation of glycerolipids.
(A) Phosphoglycerides have a glycerol backbone (coloured red) with FAs at the sn-1 and sn-2 position (coloured blue) and a phosphate moiety that links to a headgroup at sn-3 position (coloured green). In this example, the headgroup is choline and therefore the phospholipid is phosphatidylcholine (PC) (sn, stereochemical numbering). (B) The glycerol backbone with three FAs is called TAG. The glycerol backbone with two FAs is diacylglycerol (DAG). Addition of a phosphate to DAG makes phosphatidic acid (PA), the simplest phospholipid. Different headgroups (R) can be attached to the phosphate; addition of choline makes PC, ethanolamine makes phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), serine makes phosphatidylserine (PS) and inositol makes phosphatidylinositol (PI).