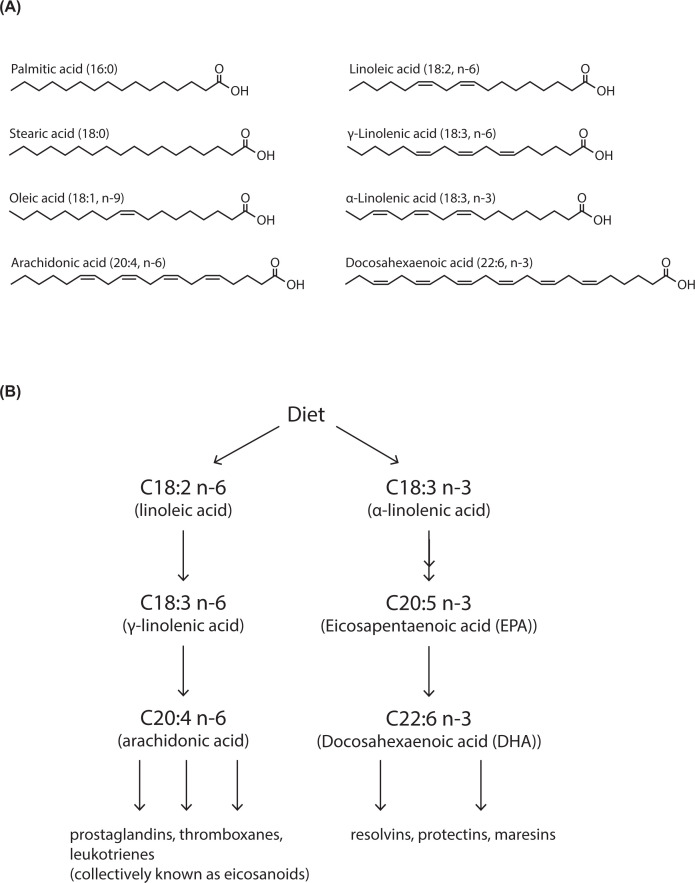
Figure 4. FA diversity due to chain length and degree of unsaturation.
(A) FAs comprise a carbon acyl chain with a carboxylic acid at one end. FAs are defined by their acyl chain length and by the number of double bonds. Thus, oleic acid is (C18:1 n-9). C18 denotes the length of the carbon chain and the number of double bonds is indicated after the colon. The position of the first double bond is denoted by n (number) where the carbon chain is counted from the hydrocarbon end. (B) Linoleic acid (C18:2 n-6) and α-linolenic acid C18:3 n−3) are essential FAs and are acquired from the diet. They can be further elongated by addition of acetyl groups by elongase enzymes and double bonds added by desaturase enzymes. n-3 and n-6 FAs are also known as ω3 and ω6 FAs, respectively. See Box 1 for explanation for the nomenclatures used for the position of the double bonds.