Figure 1.
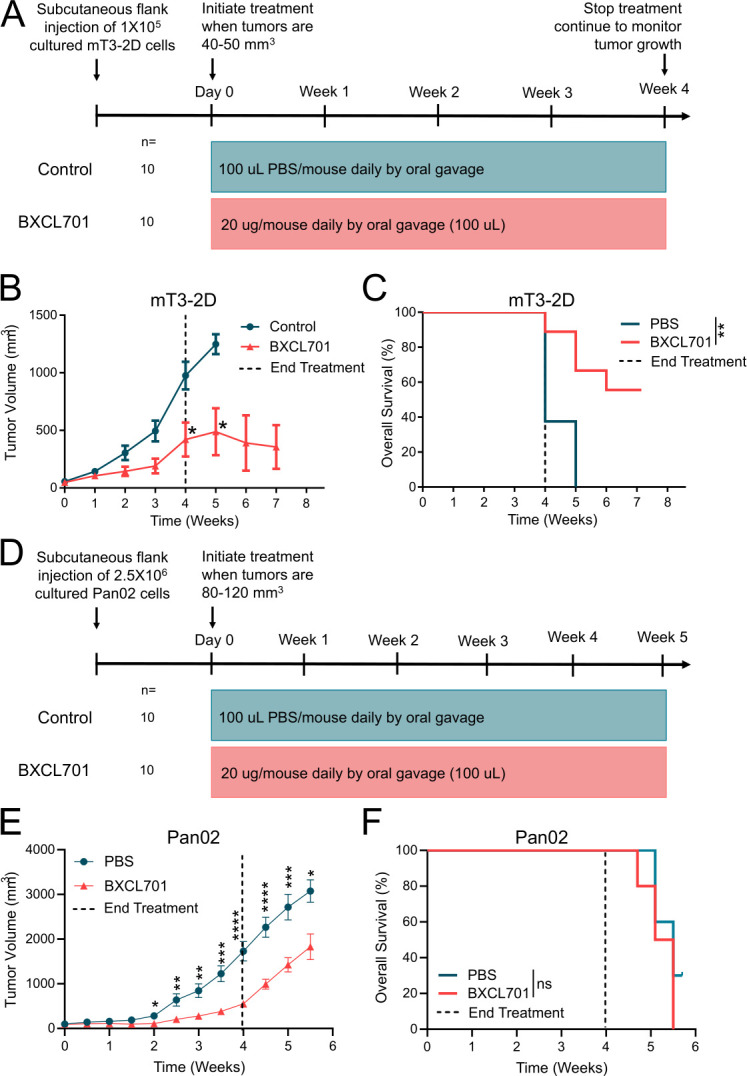
DPP inhibition reduces murine PDAC tumor growth. (A) Schematic representation of in vivo experimental design testing BXCL701 treatment vs PBS controls in mT3-2D PDAC tumors. (B) Average mT3-2D tumor growth curves in C57BL/6 mice (n=10 per group) treated with PBS control or BXCL701 for 4 weeks. Dashed line represents the end of treatment. Tumor growth was monitored weekly. (Data represented as mean±SEM. *p<0.05 as determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test). (C) Survival curves of C57BL/6 mice (n=10 per group) treated with PBS control or BXCL701 for 4 weeks. Dashed line represents the end of treatment. (**p<0.01 as determined by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test). (D) Schematic representation of in vivo experimental design testing BXCL701 treatment vs PBS controls in Pan02 PDAC tumors. (E) Average Pan02 tumor growth curves in C57BL/6 mice (n=10 per group) treated with PBS control or BXCL701. Tumor growth was monitored twice weekly. (Data represented as mean±SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 as determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test). (F) Survival curves of C57BL/6 mice (n=10 per group) treated with PBS control or BXCL701 for 4 weeks. Dashed line represents the end of treatment. (ns=nonsignificant as determined by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test). DPP, dipeptidyl peptidase; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
