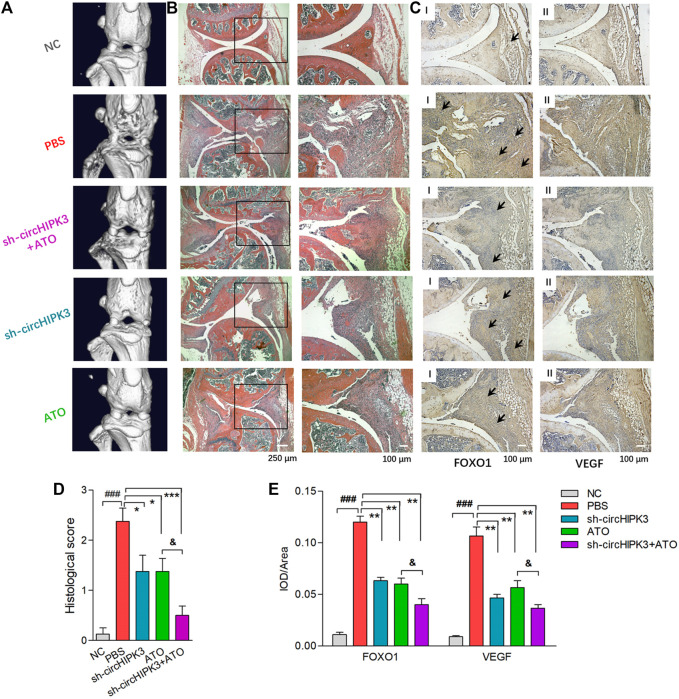
FIGURE 6.
Histological evaluation of single or combined treatment of AAV-sh-circ-HIPK3 and ATO. (A) Micro-CT images of knee joints demonstrated the destruction of bone and cartilage in CIA mice, and ATO injection alleviated the joint destruction. AAV-sh-circHIPK3 combined with ATO could significantly reduce the damages of bone compared to ATO therapy alone. (B) The severity of arthritis in CIA mice was assessed by H&E staining of knee joint sections. ATO treatment at 2.0 mg/kg/day and AAV-sh-circHIPK3 injection, respectively, significantly reduced synovial hyperplasia, cartilage/bone erosion and joint inflammation compared with CIA control mice. Additionally, the combination therapy of ATO and AAV-sh-circHIPK3 yielded more reduction of pannus formation and inflammatory infiltration. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of AAV-sh-circHIPK3 and ATO on FOXO1 (Ⅰ) and VEGF (Ⅱ) expression in synovial tissues of CIA mice. CIA mice under PBS treatment had significantly increased staining intensity of FOXO1 and VEGF compared with normal mice. And the injection of AAV-sh-circHIPK3 or ATO significantly decreased staining for FOXO1 and VEGF compared with CIA control mice. Interestingly, FOXO1 and VEGF staining in the combined treatment of AAV-sh-circ-HIPK3 and ATO group were significantly weaker than those in the CIA mice under ATO therapy alone. Histological scores (D) and average IOD values for FOXO1 and VEGF immunostaining in the knee joint synovium (E) were, respectively, evaluated and shown (n = 5; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus PBS treatment group; ###p < 0.001 versus NC; and p < 0.05 versus ATO group). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. NC = normal control group.