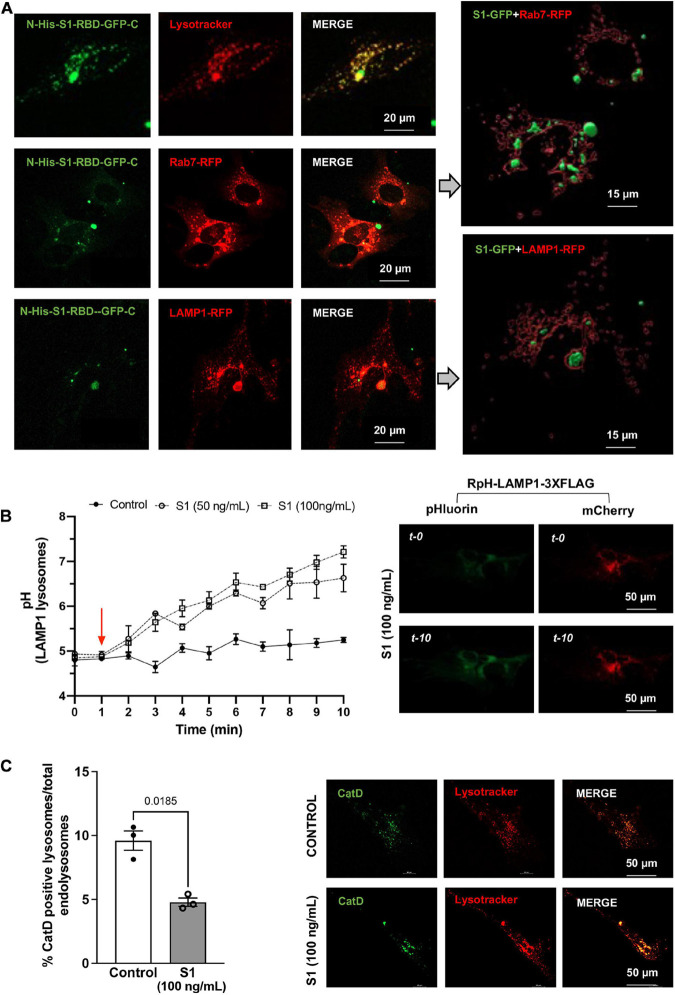
FIGURE 2.
SARS-CoV2 S1 protein entered endolysosomes and induced lysosome dysfunction in human neurons. (A) Representative confocal images show the accumulation of SARS-CoV2 S1 Receptor Binding domain (RBD) with C-terminal GFP (S1-RBD-GFP, 250 ng/mL for 48h) in endolysosomes of primary human cortical neurons. Endolysosomes were identified with LysoTracker Red DND-99 or transduced with Rab7-RFP for late endosomes and Lysosome-RFP for lysosomes. 3D Imaris reconstruction of images show the presence of S1-RBD-GFP inside late endosome (Rab7-RFP) and lysosomes (LAMP1-RFP). (B) Graph shows time-dependent lysosome de-acidification effects of SARS-CoV2 S1 (50 and 100 ng/ml) in primary human neurons and lack of de-acidification effects of heat-inactivated S1 (controls). Lysosome pH was measured ratio-metrically by transfecting with RpH-LAMP1-3XFLAG. Representative confocal images of RpH-LAMP1-3XFLAG transfected human primary neurons at 0- and 10-min were shown on the right (n = 3 repeats). (C) Representative confocal images and bar graph show that SARS-CoV2 S1 (100 ng/ml for 30 min) decreased the percentage of active cathepsin D positive lysosomes (BODIPY FL-Pepstatin A-green) vs. total endolysosomes (LysoTracker Red) in primary human cortical neurons (n = 3).