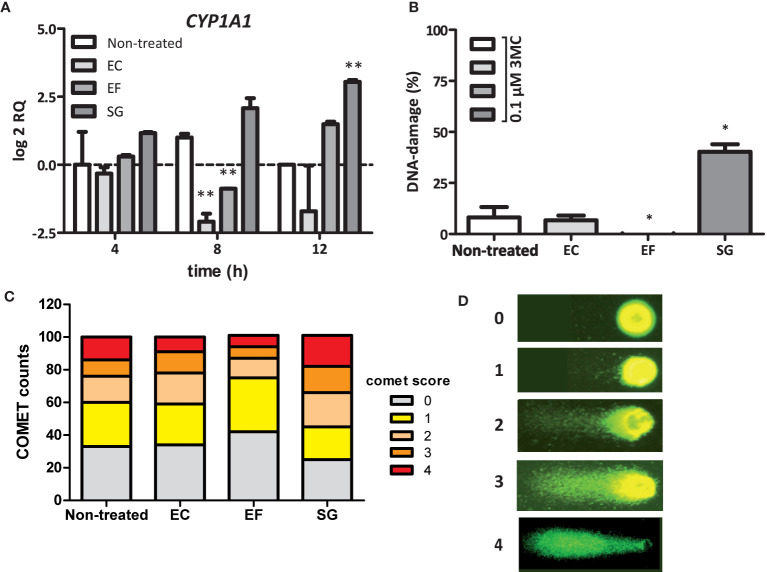
Figure 4.
SGS induced CYP1A1 expression and increase in the DNA-damaging effect of 3MC. (A) Expression of CYP1A1 in Caco-2 cells was examined by qPCR after exposure of these cells to the secretomes of E. coli NTB 5 (EC), S. gallolyticus UCN34 (SG), and E. faecalis 19433 (EF). Note that only exposure to secretomes from S. gallolyticus UCN34 resulted in increased CYP1A1 levels after 8 and 12 h (**p < 0.01). (B) DNA damage under the conditions described in Panel (A) were measured by the COMET assay (*p< 0.05). To induce low levels of DNA damage, incubation was prolonged for 18 h after addition of 0.1 µM 3MC to the culture medium. Reference ranges were determined by the incubation of Caco-2 cells without 3MC (0% damage) and with 100 µM H202 (100% damage). Only exposure to SGS from S. gallolyticus UCN34 in combination with 3MC yielded increased levels of DNA damage compared to 3MC alone (non-treated). (*p < 0.05) (C) The increase in DNA damage by SGS in combination with 3MC is mainly due to an increased number of cells with DNA damage and with high levels of DNA damage (COMET scores 3 and 4). Two-way-ANOVA (p < 0.01). (D) Representative fluorescence microscope images with assigned COMET scores used for the quantification of DNA damage as shown in (B, C).