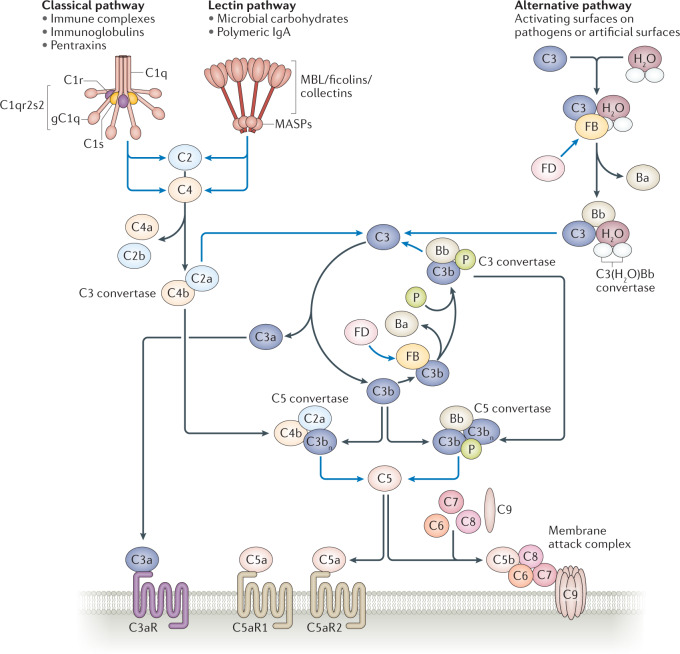
Fig. 2. Overview of the complement system.
The complement system is a network that can be divided into the classical, lectin and alternative pathways. The classical pathway is activated when C1s within the C1qr2s2 complex cleaves C2 into C2a and C2b and cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b. Likewise, in the lectin pathway, mannose-binding lectin (MBL) serine protease 1 (MASP1) and MASP2 can also cleave C2 and C4. The classical and lectin pathways converge at the level of C2 and C4 cleavage, where a complex between C2a and C4b forms the C3 convertase. The alternative pathway exhibits a constant low-grade activation on biological surfaces whereby hydrolysed C3, C3(H2O), binds to factor B (FB), which is cleaved by factor D (FD) into the Bb and Ba fragments. The Bb fragment contributes to the formation of the initial convertase C3(H2O)Bb. This convertase cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. C3b forms a complex with FB, which is again cleaved by FD into Bb, to form C3bBb, the C3 convertase. This convertase is stabilized by properdin (P). The formation of C3 convertases (C4b2a in the classical and lectin pathways and C3bBb in the alternative pathway) is amplified by the C3b-generation amplification loop (centre). By addition of extra C3bs to the C3 convertases, these are transformed into C5 convertases. C5 convertases cleave C5 into C5a and C5b, which promotes the assembly of the pore-forming unit C5b-9 within the cell membrane; this process is called the ‘terminal lytic complement pathway’. Binding of C3a to the receptor C3aR and of C5a to the C5a receptors C5aR1 and C5aR2 induces potent inflammatory responses. Blue lines depict enzymatic activity. Black lines depict binding or conversion into cleavage products. gC1q, globular head of C1q.