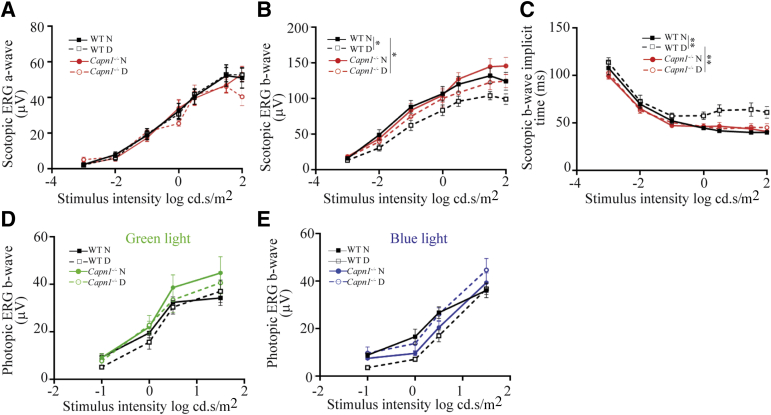
Figure 8.
Physiologic testing on the effects of Capn1 deletion on retinal function. ERG response functions were recorded to evaluate the impact of Capn1 deletion and diabetes on retinal function under scotopic conditions; both a-wave (A), b-wave (B), and scotopic b-wave implicit time (C), and photopic b-wave for green (D) and blue (E) light. In WT mice, 2 months of diabetes significantly reduced scotopic b-wave and increased scotopic implicit time when compared with nondiabetic controls; the deletion of Capn1 significantly inhibited the reduction of scotopic b-wave and the increase of scotopic b-wave implicit time in diabetic Capn1−/− mice. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 10 to 14 eyes. ∗P ≤ 0.05, ∗∗P ≤ 0.01. D, diabetic; ERG, electroretinographic; N, nondiabetic; WT, wild type.