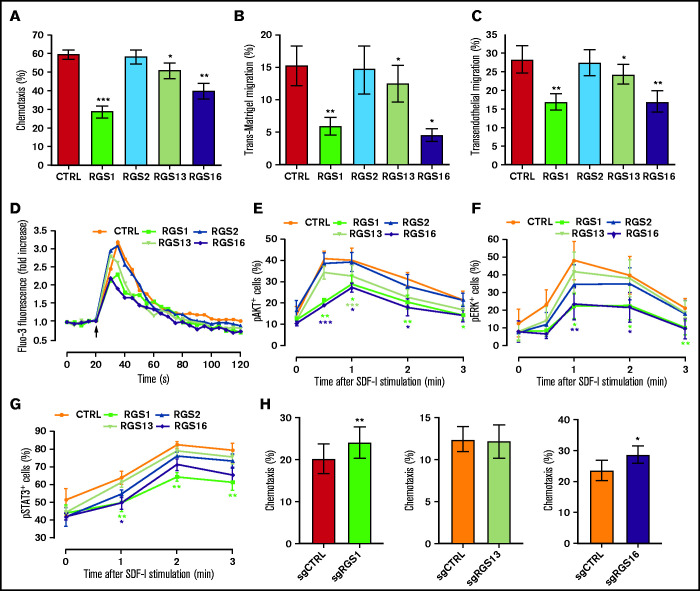
Figure 2.
R4 RGS suppress SDF-1–directed functions and signaling in HSPCs. (A-B) R4 RGS reduce HPSC motility. Chemotaxis transwell (A), trans-Matrigel (B), and transendothelial migration assays (C) were conducted using CD34+ cells transduced with control or RGS overexpression vectors in response to an SDF-1 gradient (n = 4-5). (D) R4 RGS decrease calcium flux. Transduced CD34+ cells were loaded with Fluo-3 AM and monitored for calcium mobilization before and after SDF-1 challenge. (E-G) R4 RGS inhibit SDF-1–mediated phosphorylation of signal transducers. Transduced CD34+ cells were stimulated with SDF-1 for the indicated time duration. Levels of phosphorylated AKT, ERK, and STAT3 were measured by intracellular staining with Phosflow antibodies (n = 4-5). (H) R4 RGS knockout reverted HSPC migration. CD34+ cells were electroporated with control sgRNA targeting the adeno-associated virus integration site 1 (AAVS1) or sgRNAs targeting R4 RGS to achieve loss of function, followed by chemotaxis assay (n = 4). SDF-1 at 100 ng/mL was applied for in vitro functional assays. Statistics: 2-tailed, paired Student t test. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.