Figure 1.
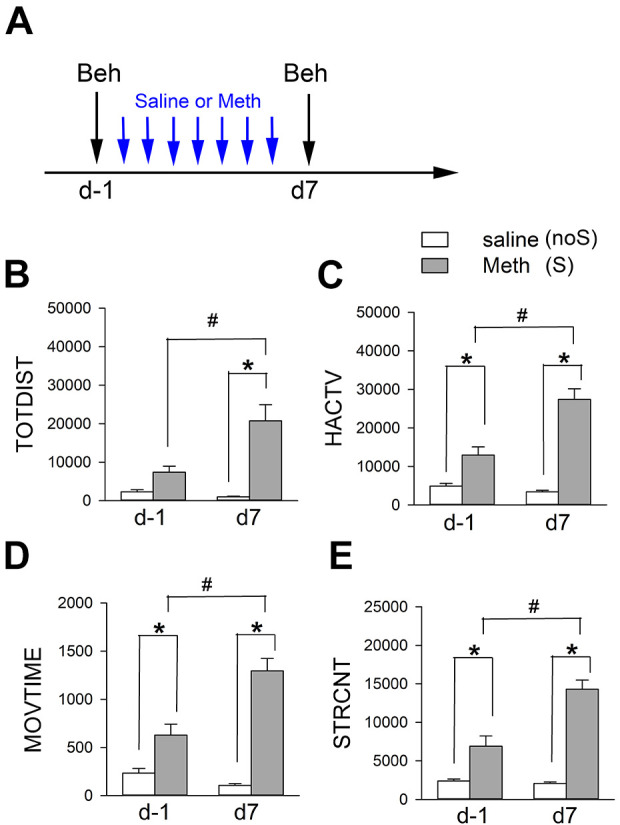
Chronic treatment with Meth induces behavioral sensitization. (A) Timeline (induction of Meth sensitization). Animals were separated into two groups. Mice in the sensitized group (S) were stimulated with a daily dose of Meth (2.5 mg/kg/d, from day 0 to day 6) while the control animals (noS) received daily saline (day 0 to day 6). (B–E) The locomotor activity was recorded for one hour after injection of low dose of Meth (1 mg/kg, S group) or saline (noS group) on days -1 and 7. Meth significantly increased locomotor and stereotype behaviors than saline control on day -1 and day 7 (S vs. noS). Meth-induced hyperactivity was further enhanced after repeated injection of Meth on day 7 (#P < 0.05, day 7 vs. day -1; *P < 0.05, Meth vs. saline, two-way ANOVA+NK test).
