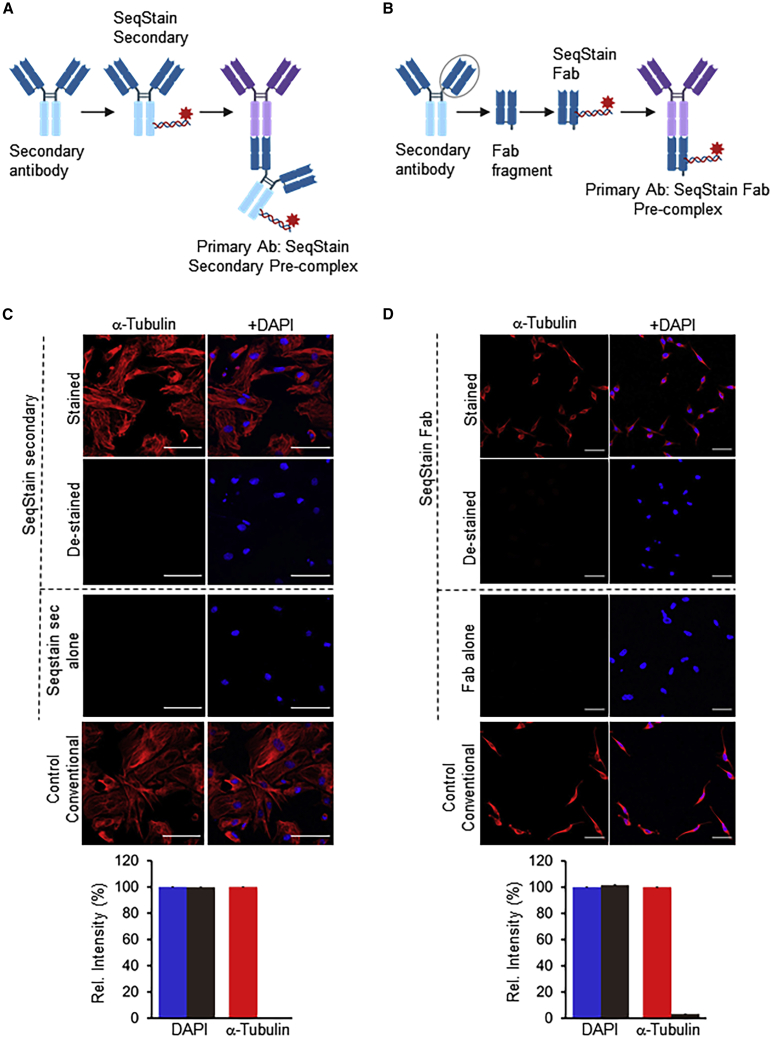
Figure 2.
Application of SeqStain secondary antibodies and SeqStain Fabs in multiplex staining
(A) Schematic representation of SeqStain secondary antibody-based multiplex imaging method. Anti-Fc secondary antibodies are labeled with fluorescent DNA to develop SeqStain secondary antibodies. Subsequently, the SeqStain secondary antibodies are pre-complexed with appropriate primary antibodies and used in staining.
(B) Schematic representation of SeqStain Fab-based multiplex imaging method. Fab fragments generated by enzymatic digestion of antibodies are labeled with fluorescent DNA to develop SeqStain Fabs. Subsequently, SeqStain Fabs are pre-complexed with their corresponding primary antibodies for use in multiplex staining.
(C) Immunofluorescence images of murine podocyte cell line stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody pre-complexed with SeqStain secondary antibody (left panels) and with DAPI nuclear staining (right panels). Immunofluorescent images after de-staining with DNase I are shown below each panel. Control staining of these cells with SeqStain secondary alone and with conventional methodology is shown in the bottom panels. All images are representative of at least two replicates. A graph showing quantification of fluorescence intensity in each panel is also presented.
(D) Immunofluorescence images of HeLa cells stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody pre-complexed with SeqStain Fab (left panels) and with DAPI nuclear staining (right panels). Immunofluorescence images of these cells after de-staining with DNase I are shown below each panel. Control staining of these cells with SeqStain Fab alone (secondary Fab) and with conventional methodology is shown in the bottom panels. All images are representative of at least two replicates. A graph showing quantification of fluorescence intensity in each panel is also presented.
Graphs show the mean ± SD. Scale bars, 100 μm.