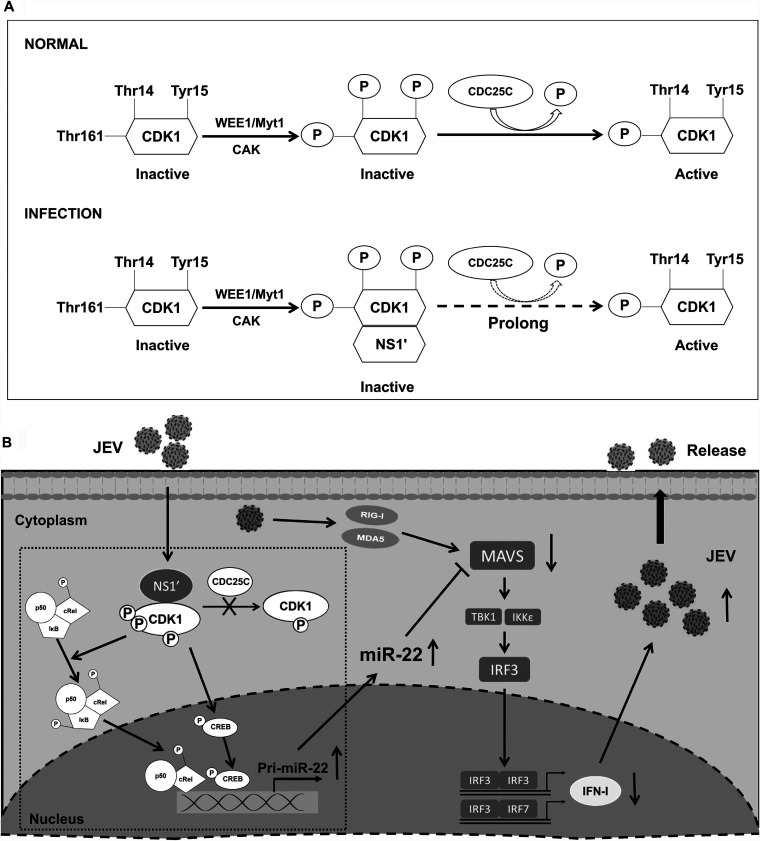
FIG 8.
Hypothetical model for the mechanism of JEV NS1′-mediated activation of CREB and c-Rel. (A) The effect of JEV NS1′ on CDK1 phosphorylation status: under the normal condition, a conserved threonine residue in the activation loop (Thr-161) of CDK1 is phosphorylated by CAK, and two sites in the ATP-binding pocket (Thr-14 and Tyr-15) are dephosphorylated. Both of these sites of CDK1 are then phosphorylated by kinases of the Wee1/Myt1 family, and subsequently dephosphorylated by phosphatases of the CDC25C, during JEV infection, and JEV NS1′ interacts with CDK1 and interrupts the CDC25C phosphatase-mediated dephosphorylation of CDK1, which prolongs the phosphorylation status of CDK1. (B) Mechanism of JEV NS1′-mediated activation of CREB and c-Rel. NS1′ protein interacts with CDK1 in host cells to prolong the phosphorylation status of CDK1, which promotes the activation of CREB and c-Rel and leads to increased expression of miR-22. miR-22 reduces the IFN-I production by targeting MAVS. The schematic in the dotted box represents the mechanism demonstrated in the present study, and the other part indicates the mechanism that has been clarified in our previous study (14).