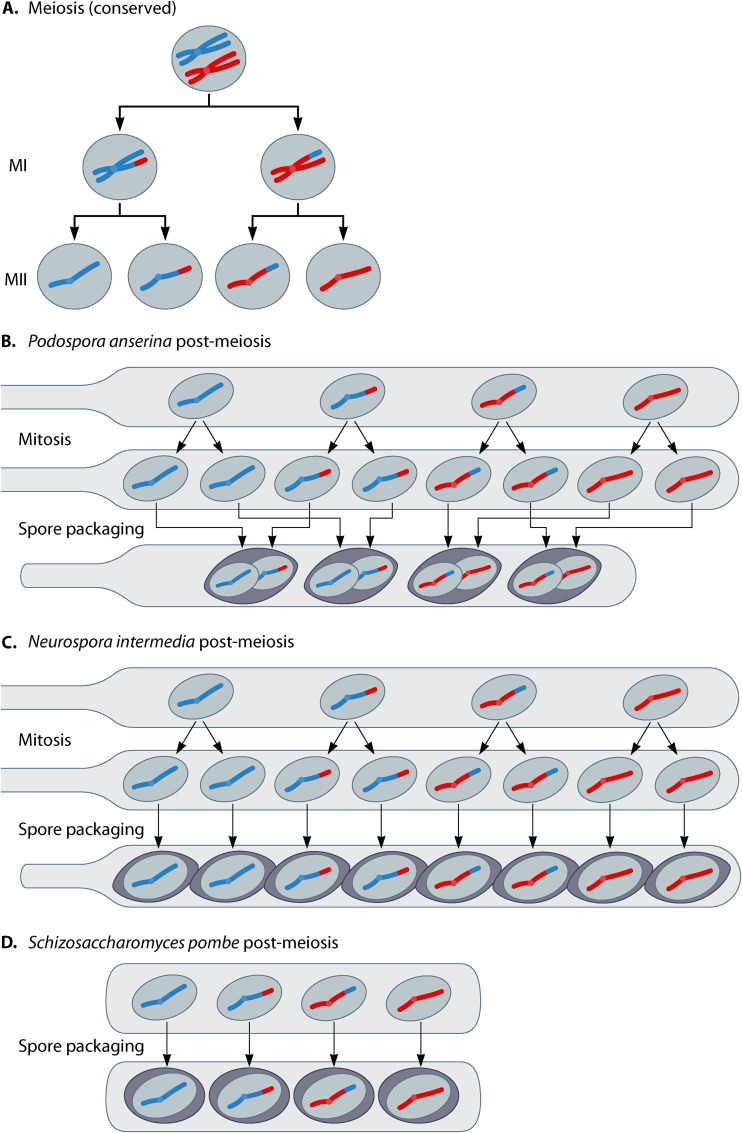
FIG 1.
Meiosis and spore packaging in select ascomycetes. (A) The basic steps of meiosis are shown for a hypothetical nucleus with one pair of homologous chromosomes. The products of the first and second meiotic divisions are abbreviated MI and MII, respectively. (B) In Podospora anserina, the products of MII undergo a mitotic division prior to packaging into four spores by following the indicated patterns. There are two segregation patterns for alleles that are particularly important for spore-killing phenotypes in Podospora. Heterozygous alleles undergo first-division segregation (FDS) if they are pulled to opposite poles during the first meiotic division. Alleles that undergo FDS are packaged into separate spores (e.g., in the diagram, chromosomes in each spore have either blue short arms or red short arms, not both). Heterozygous alleles undergo second-division segregation (SDS) if they are separated at the second meiotic division. After spore packaging, all alleles demonstrating SDS are found in all spores (e.g., in the diagram, each spore inherits both a blue and a red long-arm telomere allele). (C) In Neurospora intermedia, the meiotic products also undergo a mitotic division, but each of the resulting eight nuclei is packaged into individual spores. (D) In Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the four products of meiosis are directly packaged into spores.