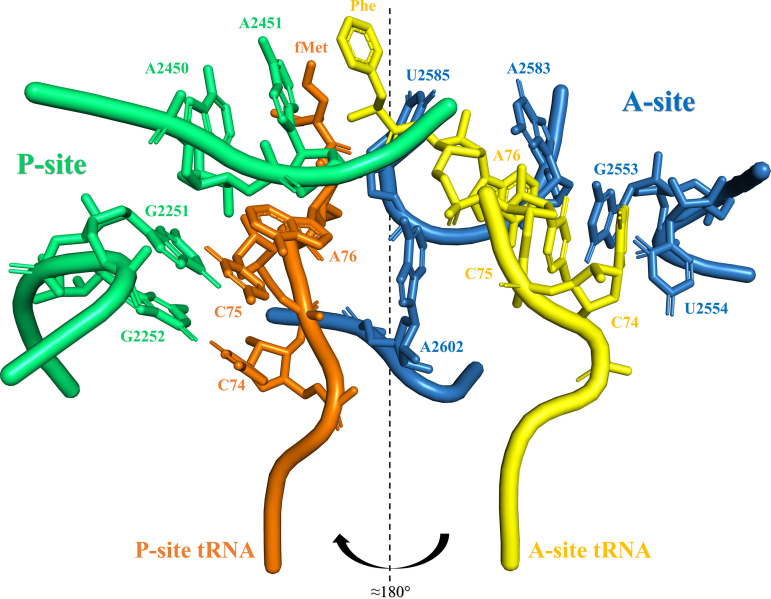
FIG 2.
Closeup view of PTC with P-site and A-site tRNAs associated. View of some of the nucleotides that coordinate the CCA end and the amino acid residue that is carried by the P-site and A-site tRNAs. P-site rRNA chain and residues are colored green, and A-site rRNA chain and residues are colored blue. P-site tRNA is colored orange, while A-site tRNA is colored yellow. The CCA end of P-site tRNA is mainly coordinated by the Watson and Crick (WC) base pairs of G2252:C74 and G2251:C75, while an A-minor interaction of A76 with A2450 from the P-site tRNA is established. Both P-site residues A2450 and A2451 are considered important to the transpeptidation reaction. The CCA end of A-site tRNA is mainly stabilized by WC base pair G2553:C75, while U2554 establishes a hydrogen bond with C74. A2583 creates an A-minor interaction with A76 from the A-site tRNA. The “rotatory motion” mechanism implies that the 3′ end of the tRNA passage moves in a helical motion of almost 180° coupled with peptide bond formation. The tRNA transitions from the A- to the P-site along a rotation axis and around U2585 and A2602. This figure was created from the crystal structure NCBI ID 4WPO, using the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 2.0 (Schrödinger, LLC).