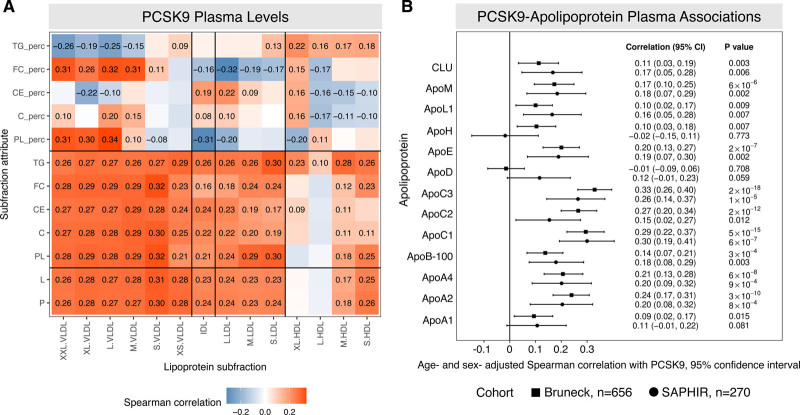
Figure 1.
Integrated lipoprotein analysis in plasma. A, Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) lipoprotein analysis and targeted apolipoprotein profiling was conducted in the Bruneck study (n=656). Plasma PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) levels, as measured by ELISA, were correlated against NMR lipoprotein attributes including; particle number (P), lipid contents (L), phospholipids (PL), total cholesterol (C), cholesterol esters (CE), free cholesterol (FC), triglycerides (TG), and lastly, each lipid class is also represented as a percentage of total lipids (perc). The lipoprotein particles are resolved by size: extremely large (XXL); extra large (XL); large (L); medium (M); small (S); and very small (XS). Only correlations with a P<0.05 are represented. Each Spearman coefficient is displayed. B, Plasma PCSK9 levels were correlated with the apolipoprotein profiles as measured by targeted mass spectrometry with authentic heavy standards in both the Bruneck (n=656) and SAPHIR (Salzburg Atherosclerosis Prevention Program in Subjects at High Individual Risk; n=270) cohorts. Note the strong association of PCSK9 plasma levels with C apolipoproteins. P values were not adjusted for multiple testing. Overall, 26 tests were performed, for 13 apolipoproteins in each of the 2 cohorts. The Bonferroni adjusted threshold of significance (at the 0.05 level) is 0.0019. CIs are bootstrap percentile CIs based on 1000 bootstrap resamples. CLU indicates clusterin (apolipoprotein J); HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; and VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein.