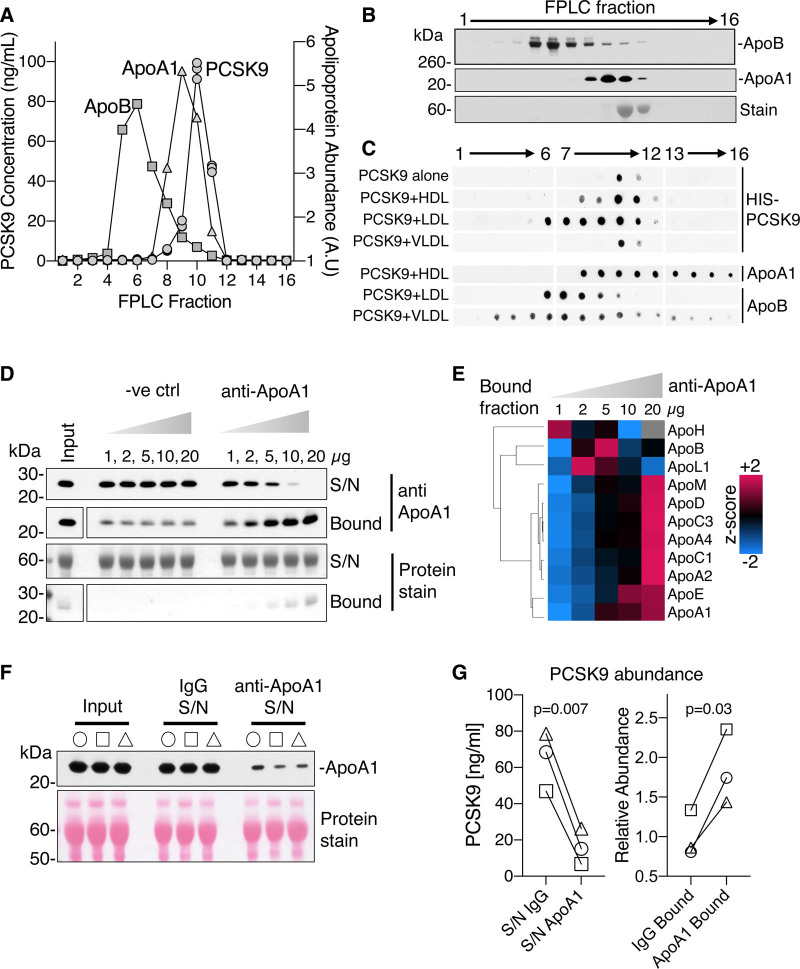
Figure 4.
Confirmation of PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9)-HDL (high-density lipoprotein) interaction. A, Pooled human plasma from healthy subjects (n=3) was separated by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and PCSK9 concentrations in collected fractions were determined by ELISA. B, Apolipoprotein abundances in SEC fractions as determined by immunoblotting. C, Recombinant HIS (polyhistidine)-tagged PCSK9 (20 µg/mL) was incubated with ucHDL (ultracentrifuge-isolated HDL), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein) before SEC separation; PCSK9 alone served as control. D, An anti–apoA1 immunoprecipitation method from human plasma was validated by immunoblotting. E, Mass spectrometry analysis of the apolipoproteins in the bound fraction of the anti–apoA1 pull downs are represented as a heat map. F, Plasma samples (10 µL, n=3 healthy volunteers) were depleted of apoA1. G, PCSK9 abundances were measured by ELISA in apoA1 depleted plasma (supernatant, S/N) and in the bound fractions. Significance was determined by a paired-Student t test. A.U indicates arbitrary units; FPLC, fast protein liquid chromatography; and ve ctrl, isotype control.