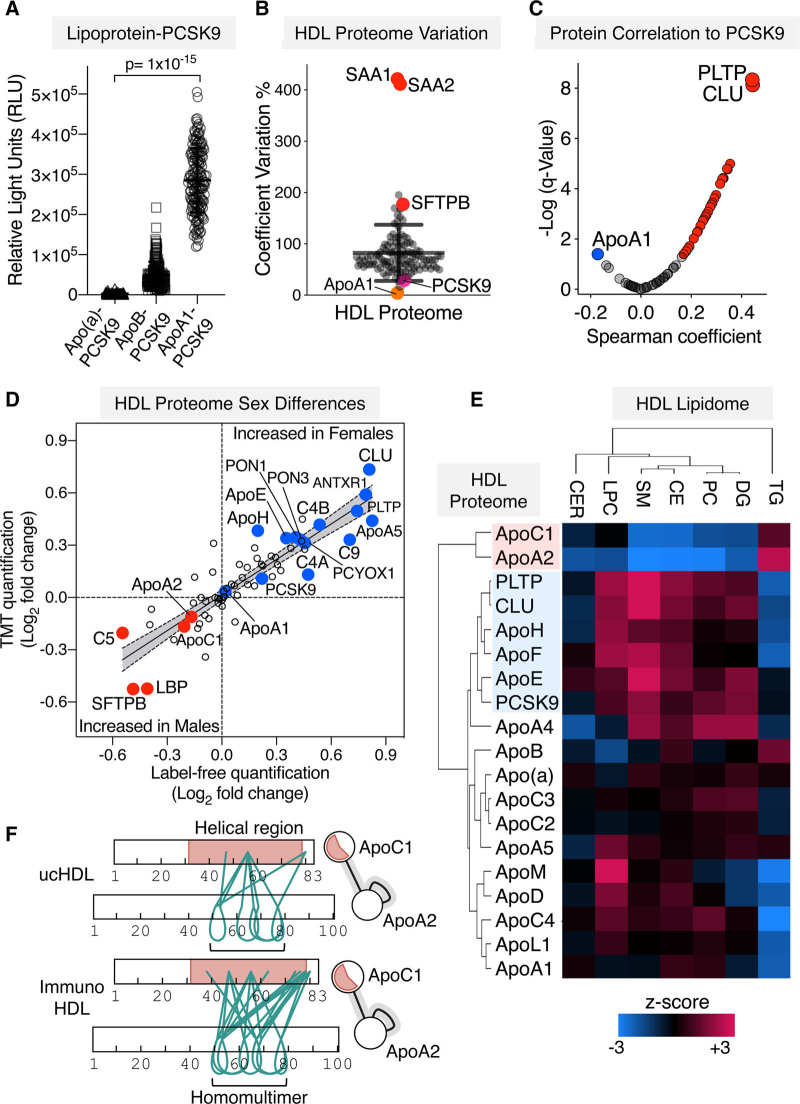
Figure 5.
Integrated proteomics and lipidomics analysis of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). A, PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) distribution across lipoprotein fractions within a cohort of 172 patients with varying CAD-related phenotypes was assessed using a modified sandwich ELISA. Significance was determined using the Kruskal-Wallis test across the groups. B, ucHDL (ultracentrifuge-isolated HDL) from these patients with CAD (n=191, including samples from patients with 6 mo follow-up) was analyzed by quantitative proteomics. The coefficients of variation in HDL protein abundances, as measured by label-free mass spectrometry (MS), were calculated across the whole cohort. C, PCSK9 protein correlations against the core HDL proteome are represented as a volcano plot. D, Quantitation by label-free and tandem-mass tag (TMT) proteomics upon ucHDL revealed proteins that were altered by sex (males, n=98. females n=66). Significant proteins in at least one method are labeled; fold changes across methodologies were compared using a linear regression analysis. E, Three hundred sixty-five lipid species were quantified in HDL by targeted MS with reference standards. A Spearman correlation matrix was generated between the sum of each lipid species in a respective class and the HDL apolipoprotein profile, as well as PCSK9, PLTP, and CLU. A hierarchical cluster analysis is represented as a heat map. F, Crosslinking mass spectrometry (XLMS) analysis of immunoHDL (immuno-isolated HDL) and ucHDL revealed a strong protein-protein interaction between apoA2 and apoC1, green lines represent crosslinks (xiview.org). AC indicates acylcarnitines; ANTXR1, anthrax toxin receptor 1; C4B, complement factor 4B; CE, cholesterol esters; CER, ceramides; CLU, clusterin; DG, diacylglycerides; LBP, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; LPC, lyso-phosphatidylcholine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PCYOX, prenylcysteine oxidase; PLTP, phospholipid transfer protein; PON, paraoxonase; RLU, relative light units; SAA, serum amyloid A; SFTPB, surfactant protein B; SM, sphingomyelins; and TG, triglycerides.