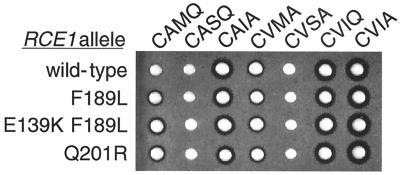
FIG. 4.
Amino acid substitutions in Rce1p that increased proteolysis of a-factor-CAMQ but did not alter proteolysis of other a-factor CaaX variants. Plasmids encoding a-factor variants with the indicated CaaX sequences (CAMQ, CASQ, CAIA, CVMA, CVSA, and CVIQ) or wild-type a-factor (CVIA) were transformed into MATa afc1 rce1 yeast strains that differ in the RCE1 allele carried on a second plasmid: wild-type RCE1 (wild type) or a mutant allele with the indicated amino acid substitution (F189L, E139K F189L, or Q210R). The relative levels of a-factor produced by these strains were evaluated by a-factor pheromone diffusion (halo) assay.