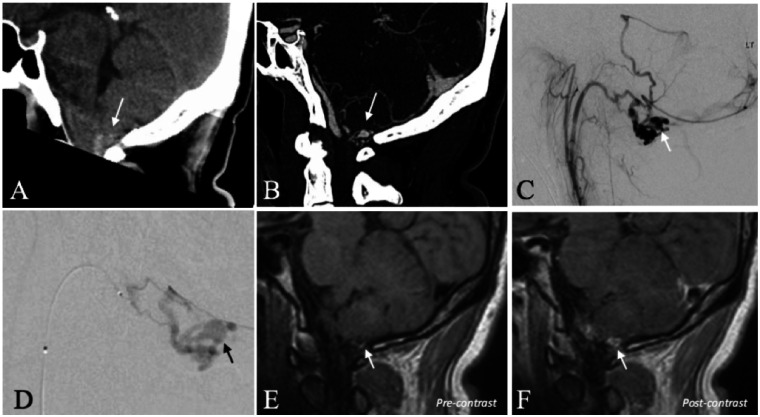
Figure 1.
A 39-year-old man with a ruptured dAVF of the hypoglossal canal. (a) CT scan (sagittal reconstruction) demonstrates acute SAH in the cerebello-medullary cistern (arrow). (b) CTA (sagittal reconstruction) demonstrates regional abnormal vascularity with a conspicuous, aneurysmal vascular out-pouching (arrow). (c) Selective injection of the ascending pharyngeal artery (DSA, lateral projection) confirms a dAVF of the hypoglossal canal. The conspicuous aneurysmal vascular structure corresponds to a venous ectasia (arrow). (d) Superselective, microcatheter injection of the hypoglossal branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery (DSA, lateral projection) better demonstrates the venous ectasia (arrow). (e) High-resolution black blood T1WI before the administration of gadolinium demonstrates hyperintense blood product contiguous with the inferior wall of the venous ectasia (arrow) consistent with the presumed site-of-rupture. (f) High-resolution black blood T1WI after the administration of gadolinium demonstrates selective, thick, concentric enhancement of the venous ectasia wall (arrow).