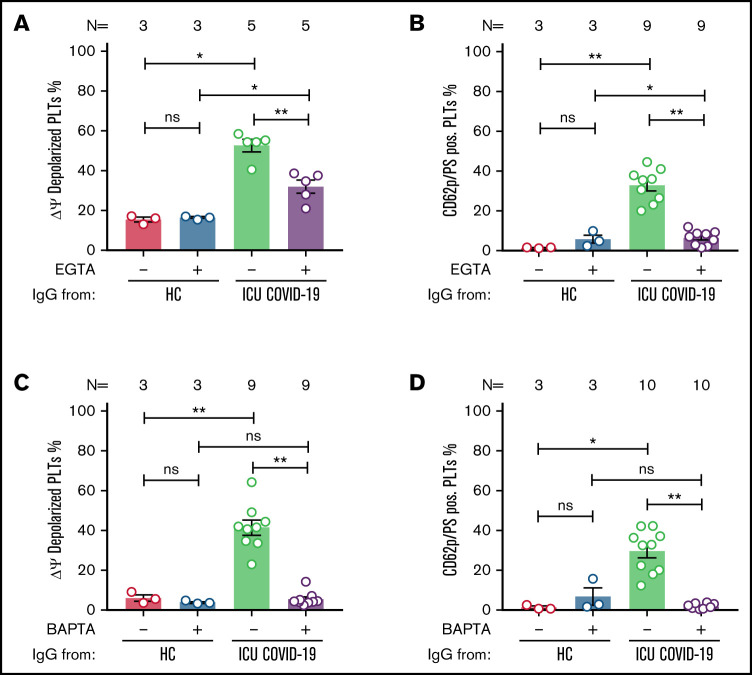
Figure 5.
ICU COVID-19 IgG-induced formation of procoagulant PLTs is dependent on calcium. Panel (A-B) shows ICU COVID-19 IgG-induced changes of different PLT markers in the presence (vehicle) or absence of extracellular calcium (EGTA 1 mM). FC detected changes of (A) PLT Δψ and (B) formation of CD62p/PS-positive PLTs after ICU COVID-19 IgG incubation in vehicle or EGTA pretreated wPLTs, respectively. (C-D) ICU COVID-19 IgG-induced PLT changes in the presence (vehicle) or in intracellular calcium depleted (BAPTA 20 µM) wPLTs. FC detected changes of (C) PLT Δψ and (D) formation of CD62p/PS-positive PLTs induced by ICU COVID-19 IgG in vehicle or BAPTA preloaded wPLTs, respectively. Data are presented as mean percentage ± SEM of (A,C) Δψ depolarized PLTs and mean percentage ± SEM of (B,D) PS (Lactadherin-FITC) and CD62p-APC-positive wPLTs. Note that lactadherine is a calcium-independent marker of PS externalization. The number of patients and healthy donors tested is reported in each graph. See Figure 1 for P values and abbreviation definitions.