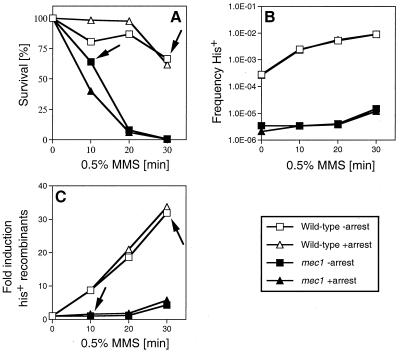
FIG. 5.
Artificial cell cycle arrest does not rescue the damage-induced recombination defect in mec1 cells. (A) Survival of wild-type cells and mec1 cells after acute exposure to 0.5% MMS for the indicated times was measured as described elsewhere (65). (B) Absolute frequencies of His+ recombinants per viable cell with respect to MMS dose in wild-type and mec1 cells. The spontaneous frequency for His+ recombinants in wild-type cells was 3.35 × 10−4 without arrest and 2.67 × 10−4 with arrest, and the values in mec1 cells were 3.45 × 10−6 without arrest and 2.1 × 10−6 with arrest. (C) Fold induction of His+ recombinants with respect to MMS dose. (A to C) Shown is one experiment typical of three to five performed. The decrease in induced recombination in mec1 cells was seen in every experiment. The wild-type strain was P7BAB, and the mec1 strain WDHY1558. The arrows in panels A and C indicate the effect on induced recombination at comparable survival levels for both strains (see text).