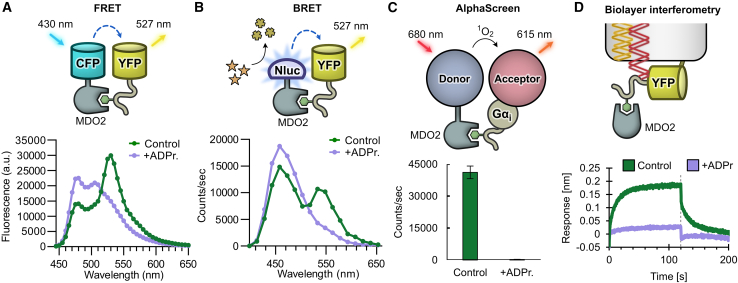
Figure 5.
Various assay technologies can be utilized to detect binding to the MARylated Gαi
(A) Measurement of interaction by FRET. Fluorescence emission spectra of CFP-MDO2 and YFP-GAP(MAR) in absence (control) or presence of 200 μM ADP-ribose (ADPr.).
(B) Measurement of interaction by BRET. Luminescence emission spectra of Nluc-MDO2 and YFP-GAP(MAR) in absence (control) or presence of 200 μM ADP-ribose.
(C) Measurement of interaction by AlphaScreen. Biotinylated MDO2 and His-tagged MARylated Gαi were mixed with streptavidin donor beads and chelate acceptor beads in absence (control) or presence of 10 μM ADP-ribose. The luminescence signal was detected upon excitation of donor beads. Data shown are mean ± standard deviation with n = 4 replicates.
(D) Measurement of interaction by biolayer interferometry. His-tagged YFP-GAP(MAR) was bound to the optical sensor surface, and the change of signal after association (0 s) or dissociation (120 s, dotted line) of unlabeled MDO2 protein was determined in absence or presence of 3.16 μM ADP-ribose.