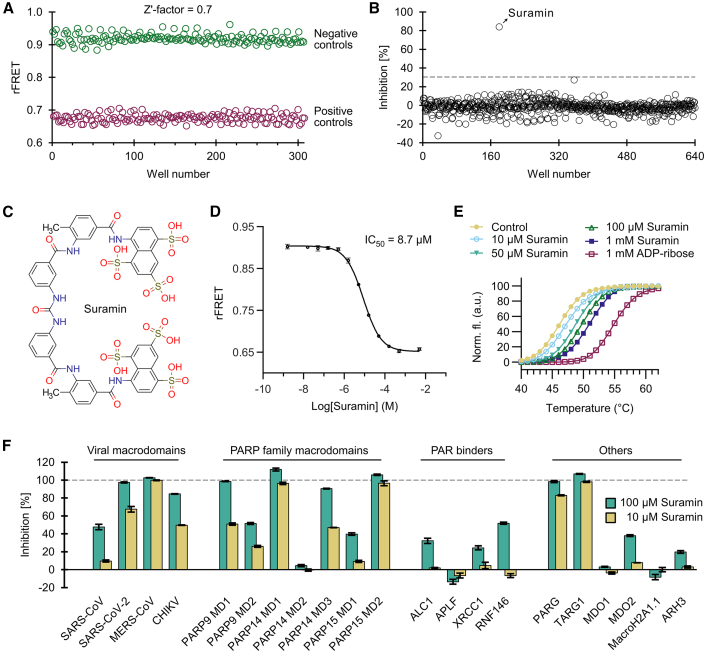
Figure 6.
Development of a screening assay for the SARS-CoV-2 nsp3 macrodomain
(A) Signal validation for a screening assay with CFP-SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 (1 μM) was mixed with 5 μM YFP-GAP(MAR) in absence (negative control) or presence (positive control) of 200 μM ADP-ribose, and a Z′ factor of 0.7 was calculated.
(B) Screen of ENZO FDA-approved drug library comprising 640 compounds. Only the compound suramin showed inhibition above 30% and was taken to further validation.
(C) Structure of the hit compound suramin.
(D) Dose-response curve with suramin shows an IC50 of 8.7 μM for the SARS-CoV-2 nsp3 macrodomain in the FRET-based assay. The control containing no compound was set one logarithmic unit below the lowest concentration, while the control containing 200 μM ADP-ribose was set one logarithmic unit above the highest suramin concentration.
(E) Suramin shows stabilization of SARS-CoV-2 nsp3 macrodomain by DSF.
(F) Inhibition profile of suramin against human and viral ADP-ribosyl binders used in this study. The inhibition was calculated based on the ratiometric FRET signals of the CFP-fused binders mixed with YFP-GAP(MAR) or YFP-GAP(PAR).
Data shown for (D) and (F) are mean ± standard deviation with n = 4 replicates.