Figure 1.
Characterization and differentiation of patient iPSC lines
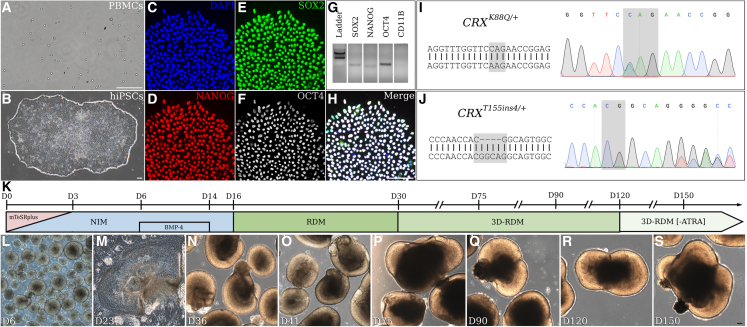
(A–S) Patient PBMCs (A) were reprogrammed to generate stable hiPSC lines (B). Immunocytochemistry was performed with antibodies against NANOG (D), SOX2 (E) and OCT3/4 (F), and cells were counterstained with DAPI (C). The merged image is shown in (H). Primers for SOX2, NANOG, OCT4, and CD11B were utilized for RT-PCR analysis (G). Sanger sequencing results for hiPSCs to confirm the presence of the CRXK88Q/+ (I) and CRXT155ins4/+ (J) variants. The retinal differentiation protocol timeline is summarized in (K), and representative images of the differentiation process are shown for the control hiPSC line (CRXWT) in (L)–(S). Scale bar (A, B, H, and S), 100 μm.