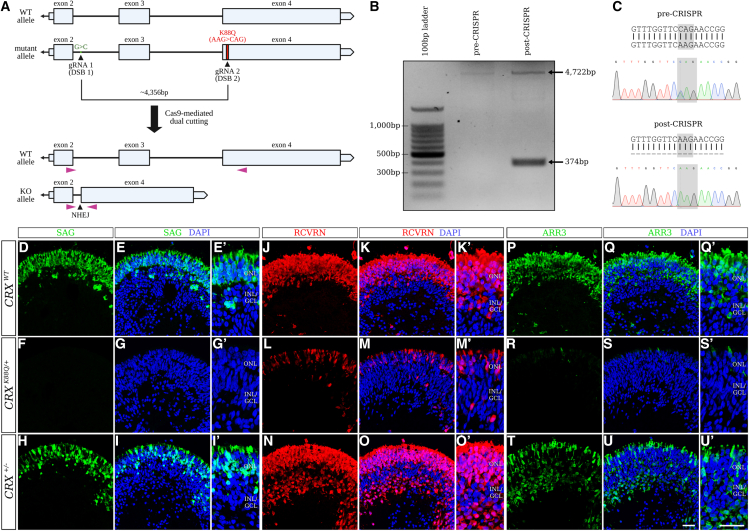
Figure 7.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of the mutant CRX allele in patient hiPSC
(A–C) The CRISPR/Cas9 dual-cutting target sites are mapped onto the mutant allele of the CRX gene (A). PCR was performed using primers shown in (A; purple triangles), revealing an additional 374-bp band representing the edited “knockout (KO) allele” after CRISPR/Cas9 editing (B). Sanger sequencing was also utilized to confirm loss of the K88Q mutation after CRISPR-mediated editing (C).
(D–U′) Immunofluorescence staining using antibodies against SAG (green; D–I′), RCVRN (red; J–O′), and ARR3 (green; P–U′) are shown for control (CRXWT; D–E′, J–K′, and P–Q′), CRXK88Q/+ (F–G′, L–M′, and R–S′), and CRX+/− (H–I′, N–O′, and T–U′) retinal organoids at D180 (n = 3 organoids per line). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars (U and U′), 100 μm. OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL/GCL, inner nuclear layer/ganglion cell layer.
See also Figures S6 and S7.