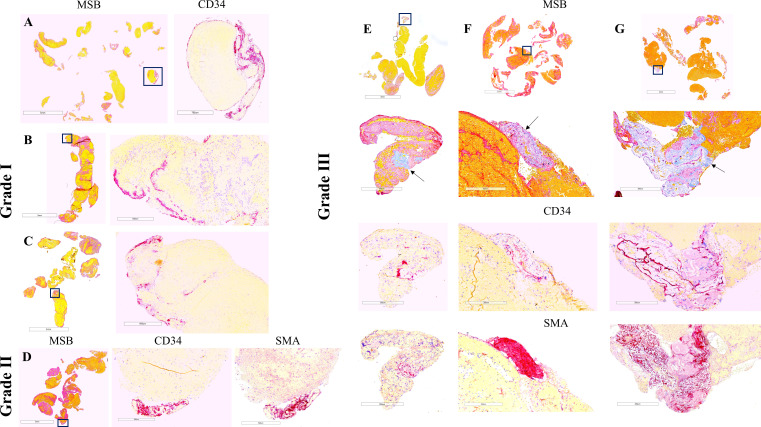
Figure 1.
Thrombus histology and immunohistochemistry in representative cases selected by the degree of vessel wall injury and mechanical thrombectomy approach. Grade I: aspiration catheter (A), stentriever (B), and combination of devices (C); grade II: stentriever (D); grade III: aspiration catheter (E), stentriever (F), and combination (G). Martius Scarlett Blue (MSB) staining identifies the standard components of clots: red blood cells (yellow), fibrin (red). and platelets/other (light pink). Collagen can be also identified by MSB (E–G: light blue and arrows). Immunostaining for CD34 and smooth muscle actin (SMA) identifies endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells (purple), respectively. Areas within the squares in the MSB images are magnified in the immunostaining images. Note that clustered endothelial cells are distributed along the edge of clot fragments in grade I injury (A–C) while defined clusters of CD34- and SMA-positive cells are located at the periphery of the clot in grade II (D) and are associated with collagen in grade III (E–G). Scale bar (MSB)=5 mm (A, C), 3 mm (B, D), 3 mm and 300 µm (E–G); scale bar (immunostaining)=700 µm (A), 500 µm (B), 600 µm (C), and 300 µm (D–G).