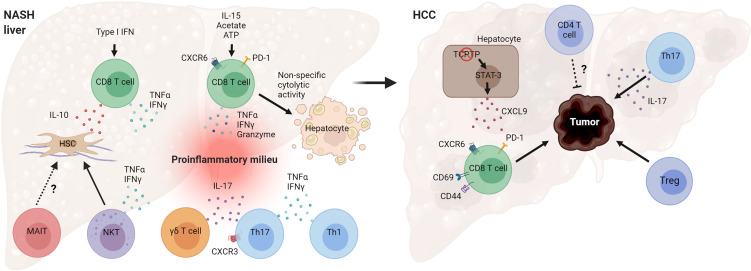
Figure 4.
Mechanisms by which T cells can promote NASH and HCC pathogenesis. Hepatic CD8 T cells in NASH secrete cytokines that promote hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and tissue inflammation. NASH-associated CD8 T cells can also cause non-specific (antigen-independent) cell death of hepatocytes. T helper cells, Th17 and Th1, and γδ T cells secrete effector cytokines during NASH, contributing to inflammatory tissue milieu. Loss of T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TCPTP) in hepatocytes leads to STAT-3-dependent secretion of CXCL9 and liver tumorigenesis. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)+ CD8 T cells, Tregs, and cytokine IL-17 promote HCC development, while CD4 T cells overall may decrease tumor burden and control tumor size. (Created with BioRender.com).