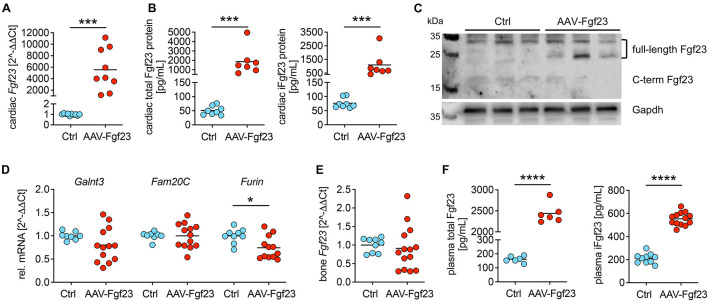
FIGURE 2.
Myocardial gene transfer of AAV-Fgf23 causes cardiac-specific Fgf23 overexpression resulting in the synthesis of intact Fgf23 protein. (A) Relative cardiac Fgf23 mRNA expression increases in AAV-Fgf23 mice compared to Ctrl. (B) ELISA-based quantification of cardiac Fgf23 protein in heart tissue lysates shows increased total and intact Fgf23 (iFgf23) protein in AAV-Fgf23 mice compared to Ctrl. (C) Representative immunoblotting of Fgf23 in cardiac tissue of three mice each demonstrates increased iFgf23 protein in AAV-Fgf23 mice compared to Ctrl, whereas C-terminal fragments are slightly reduced. Gapdh serves as the loading control. (D) Relative mRNA expression of Galnt3 and Fam20C is unchanged in AAV-Fgf23 mice compared to Ctrl, while Furin transcription is significantly reduced. (E) Fgf23 mRNA expression in the bone is similar between AAV-Fgf23 and Ctrl mice. (F) Plasma C-term and iFgf23 levels are significantly enhanced in AAV-Fgf23 mice compared to Ctrl. Data are given as scatter dot plots with means; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 analyzed using unpaired t-test or Mann–Whitney test according to Shapiro–Wilk normality test; n = 6–14 mice per group.