FIGURE 2.
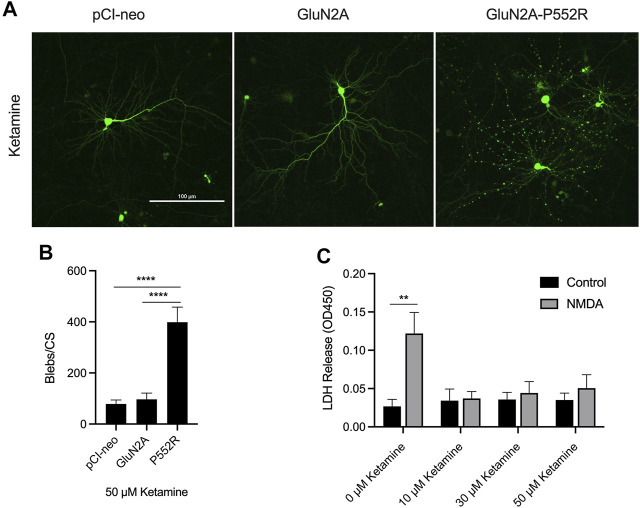
Ketamine treatment does not rescue GluN2A-P552R-mediated dendritic blebbing. Representative images of cortical neurons transfected with GFP and either pCI-neo, GluN2A, or GluN2A-P552R and co-treated with 50 µM ketamine show that GluN2A-P552R transfected neurons exhibit pronounced blebbing that is not rescued by the open-channel blocker (A). Quantification of dendritic blebbing confirmed significantly more blebs in the GluN2A-P552R group (B) (****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA/Tukey post-hoc, n = 9). LDH assays of untransfected primary cortical neurons treated with 10 µM glycine (control) or 10 µM glycine + 30 µM NMDA (NMDA) confirmed that ketamine is protective against excitotoxic injury (C) (**p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA/Sidak post-hoc, n = 3). Therefore, the failure of ketamine to rescue GluN2A-P552R dendrotoxicity is not due to inefficacy of the drug in our culture system. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Three transfections per condition were analyzed from each independent imaging experiment.