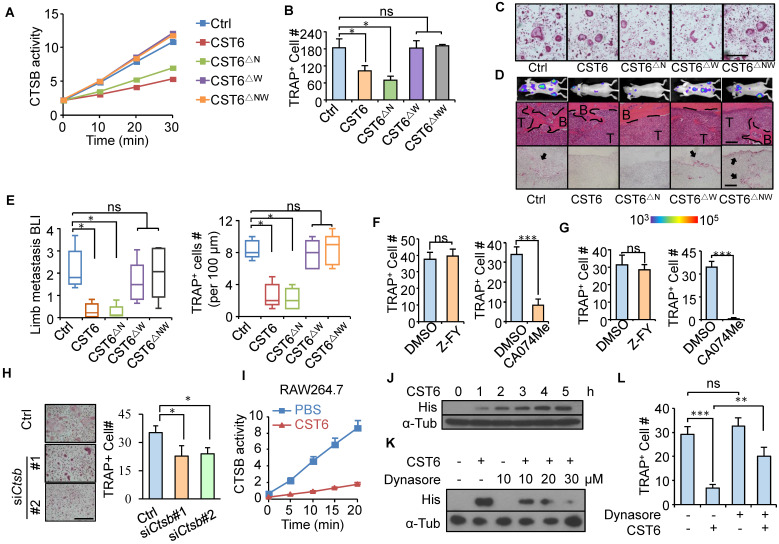
Figure 2.
CST6 regulates osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting CTSB. (A) CTSB enzymatic activity in lysates of SCP2 cells expressing wild type or mutant CST6 (n = 3 independent experiments). ∆N, N64A; ∆W, W135A; ∆NW, N64A and W135A double mutant. (B, C) Osteoclastogenesis of primary bone marrow treated with CM from SCP2 overexpressing CST6 mutants (n = 3 independent experiments). Representative images of TRAP staining were shown in C. Scale bar, 150 μm. (D, E) In vivo bone metastasis analysis of SCP2 cells expressing CST6 mutants (n = 10 mice per group). Shown are representative images of BLI, H&E and TRAP staining of bone metastases in hind legs at week 6 after SCP2 injection (D), and quantitation of BLI signal and TRAP+ cells (E). Scale bar, 200 μm. (F) Osteoclastogenesis of primary bone marrow treated with 10 μM Z-FY(t-Bu)-DMK (Z-FY) or CA-074Me (n = 3 independent experiments). (G) RAW264.7 osteoclastogenesis after treatment with Z-FY or CA074Me (n = 3 independent experiments). (H) Osteoclastogenesis of murine primary bone marrow cells transfected with Ctsb siRNA. (I) Intracellular CTSB activity of RAW264.7 after treatment with 32 nM CST6 protein. (J) RAW264.7 was cultured with recombinant His-tagged CST6 protein for the indicated time, and intracellular CST6-His level was analyzed by Western blots after PBS washing of the cells. α-Tub, α-Tubulin. (K) Western blot analysis of intracellular CST6-His level of RAW264.7 after culturing the cells with CST6-His protein and various concentrations of Dynasore. (L) RAW264.7 osteoclastogenesis after CST6 protein and Dynasore treatment. Scale bar, 150 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.