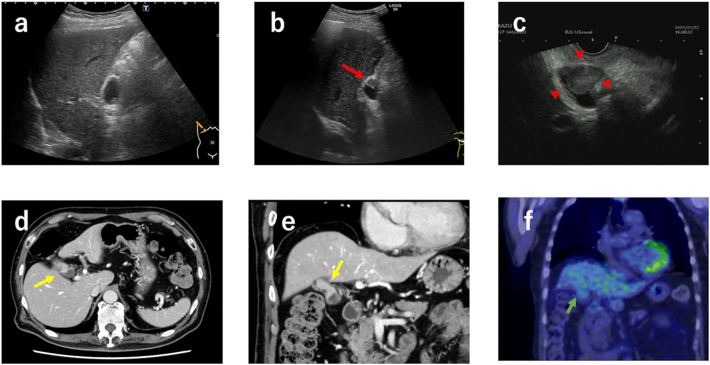
Fig. 1.
Preoperative transabdominal ultrasonography(a–b), endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) (c), computed tomography (CT) (d), EUS (e), and positron emission tomography (PET)-CT(f). (a) Previous year's transabdominal ultrasonography finding was normal. (b) In this US, wall thickening is noted (red arrow). (c) Endoscopic ultrasonography reveals subpedunculated, broad-based, elevated lesions with irregular surfaces (red arrow head). (d–e) A tumor is found that protruded into the lumen of the bottom of the gallbladder in the contrast-enhanced (yellow arrow) CT. (f) PET-CT shows mild uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) in the tumor (green arrow). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)