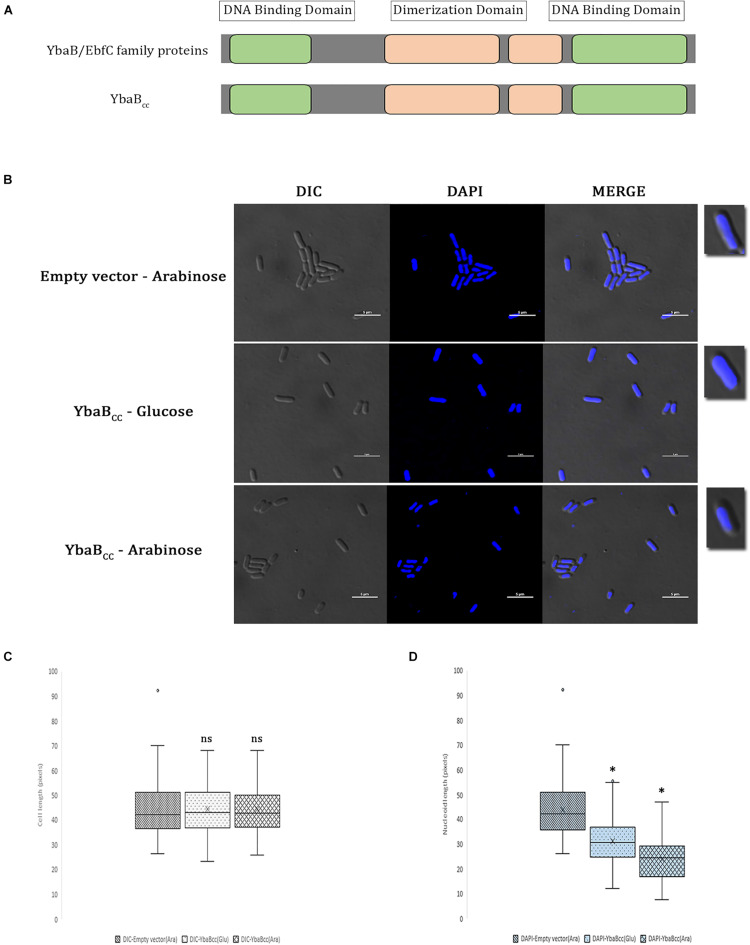
FIGURE 1.
YbaBCc binds and compacts DNA in E. coli. (A) Schematic presentation of YbaBCc protein domain organization. YbaB/EbfC family proteins show similarity in domain structures with YbaBCc. There are two DNA-binding domains present at either terminus of YbaB/EbfC family proteins, which together form a unique tweezer-like structure in order to bind to the target DNA. (B) YbaBCc overexpression in E. coli cells. YbaBCc was expressed ectopically from pBAD promoter in RP40 cells. In wild-type E. coli, nucleoid occupies the entire cytoplasmic space, whereas a compacted nucleoid tends to be away from the cell periphery and more toward the center of the bacterial cell. The scale bar represents 5 μM. (C) Box and whisker plots of mean cell length. Whiskers represent minimum and maximum cell lengths observed in each strain (1 μM = 32 pixels). Cross (x) represents mean values and horizontal line across boxes represent the median values. Analysis was done using Fiji (ImageJ) software (n, number of cells analyzed = 99 per strain, per condition). (D) Box and whisker plots of mean nucleoid length. Whiskers represent minimum and maximum nucleoid lengths observed in each strain (1 μM = 32 pixels). Cross (x) represents mean values and horizontal line across boxes represent the median values. Analysis was done using Fiji (ImageJ) software (n, number of cells analyzed = 99 per strain, per condition). (C,D) Same cells were analyzed for measuring cell lengths and nucleoid lengths. YbaBCc protein bound nucleoid reduces in length as compared to the protein-free nucleoid in non-overexpressing conditions. Box and whisker plots (n = 99 per strain) were generated for statistical analysis with the whiskers including all data points within 1.5∗IQR. ns = non-significant. ∗p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA compared to the empty vector pBAD (ara) control.