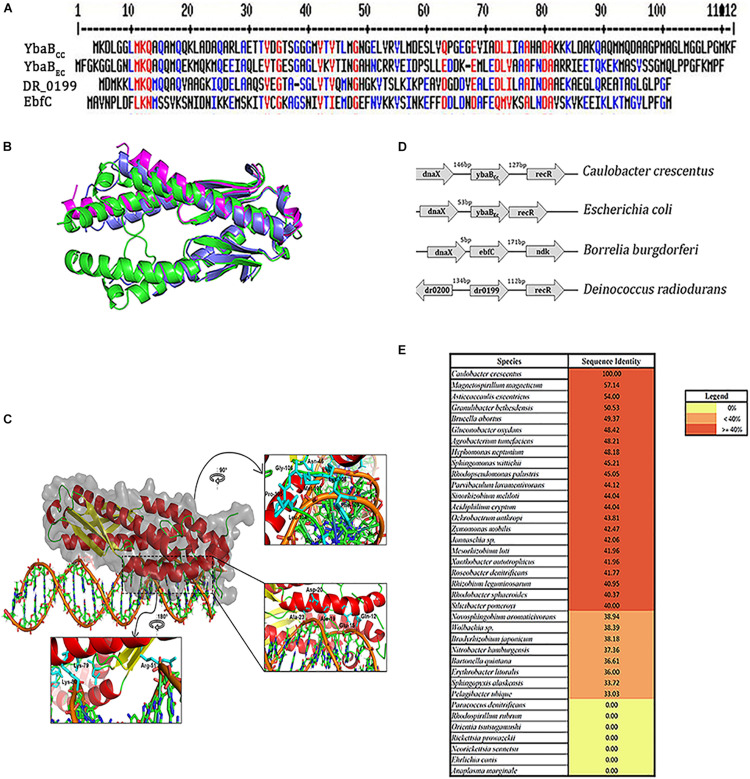
FIGURE 2.
YbaBcc is conserved across multiple bacterial species. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of YbaB/EbfC proteins from different bacterial species using MultAlin software (red—high consensus residues, blue—low consensus residues, at the given position). (B) Structural superposition of the modeled YbaBCc protein with structural homologs. The modeled protein (colored green and shown in cartoon representation) is a homodimer, as seen in the structural homologs from E. coli (PDB id: 1PUG) colored light blue. Another structural homolog from Haemophilus influenza (PDB id:1J8B) colored magenta is in monomeric form. Image made using PyMOL. (C) Protein-DNA docking model of YbaBCc (shown in cartoon and surface representation colored in secondary structure) is observed to bind to the DNA motif (5′-ATGTAACAGCTGAATGTAACAA-3′) as obtained from HADDOCK web server. The insets show the orientation of side chains of the interacting residues in stick representation (colored cyan). (D) Schematic representation of the ybaB/ebfC gene locus with adjacent genes in various bacteria. This arrangement of genes appears to be conserved in most bacteria that harbor YbaB/EbfC proteins. (E) YbaB homologs in alpha proteobacteria. Genomes displaying YbaB homologs with more than 40% sequence identity are labeled in red and proteins having identity below 40% are labeled in orange. Bacterial genomes with no YbaB homologs are labeled in yellow.